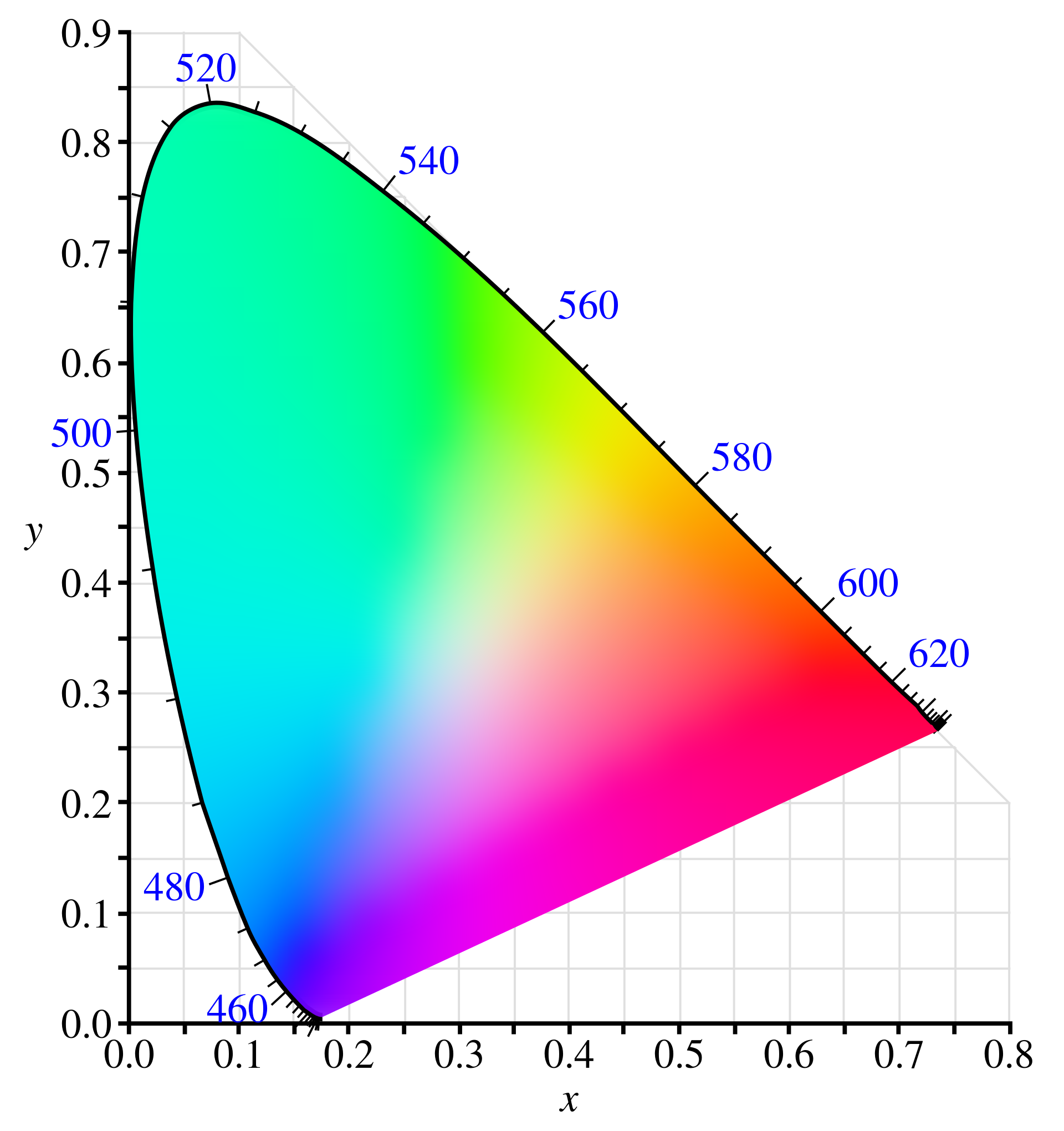Subsections of DaVinci Resolve
Configuration
Global View Settings
Save Monitor Space
- Menu Workspace → Turn OFF Show Page Navigation
Dual Monitor Config
Note
Requires DaVinci Studio license.
- Use second monitor for interface: menu Workspace → Dual Screen = ON;
- Use second monitor for full-screen view of video: menu Workspace → Video Clean Feed=.
Timeline Config
Turn ON Timeline -> Selection follows playhead
Database and files
Create a new database from scratch. Choose PostgreSQL or disk files.
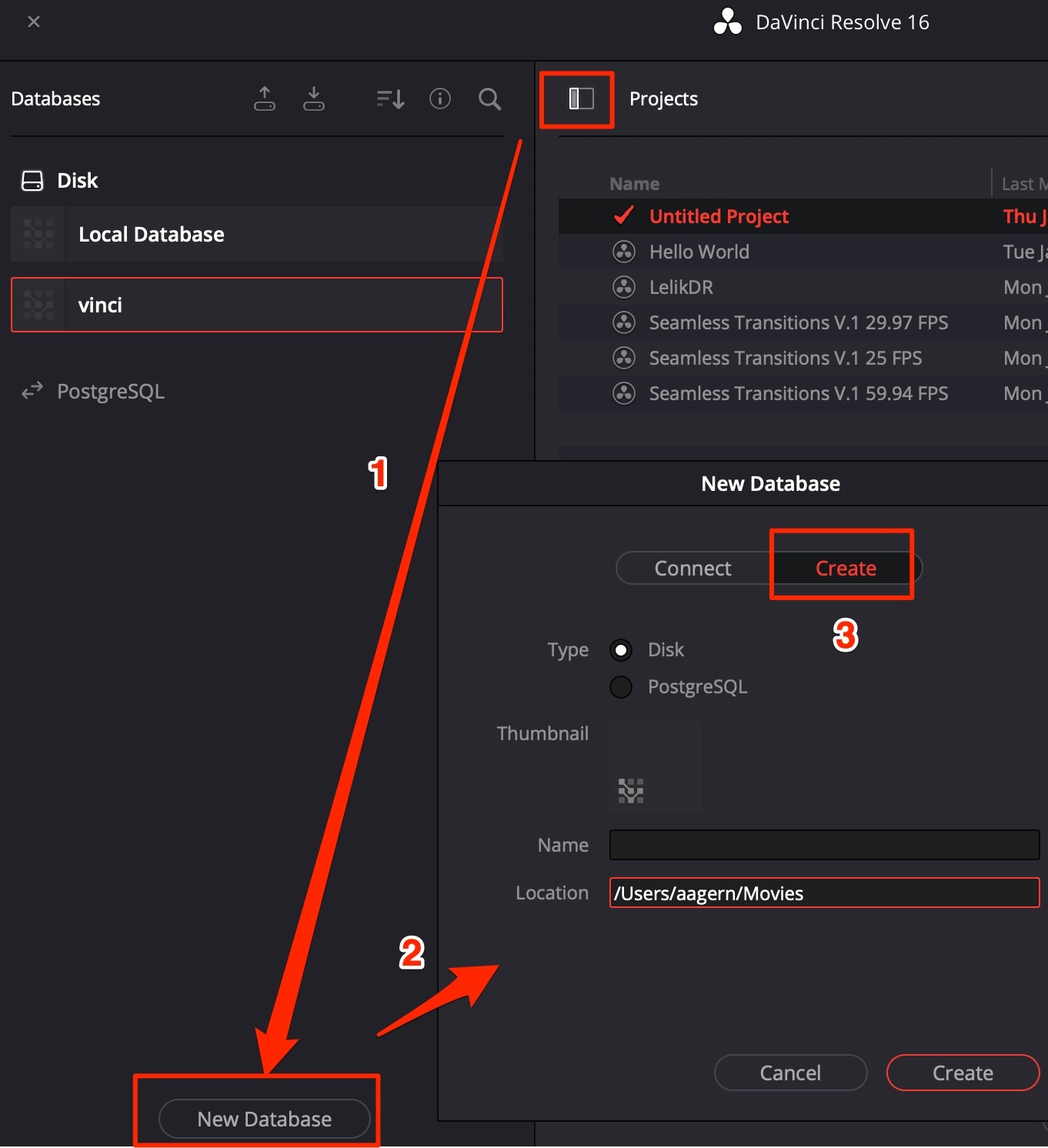

It is recommended to create a separate database + folders for video, pictures, cache etc. for each global project, like Youtube-channel.
Folder structure on disk:
-PROJECT
–Database
–Cache
–SourceMedia (source video)
–Gallery (color correction templates)
–Output (master videos)
–Backups
Project Settings
- Timeline resolution - the resolution in which the project will be edited. This is NOT the resolution, in which the project will be rendered. So you can edit the whole project in FullHD or 2048x1080DCI faster mode and then render it in 4K UHD or 4096x2160 DCI - DaVinci Resolve will mathematically scale all masks & effects to match the higher resolution on final render. Blackmagic does warn that such scale may cause some approximation;
- Timeline resolution - may be changed in process of work. Convenient to choose before work;
- Timeline frame rate - cannot be changed in process of work. Need to choose wisely! For example, transitions correction layers may be only made for specific frame rate (29.97 FPS);
- Playback frame rate the same as timeline frame rate, but is the playback rate of the connected reference monitor;
- Video Monitoring section contains parameters for the connected reference monitor;
- Optimized media resolution - may be changed later, but better to change right away to save performance and space on disk = Half/Quarter from original;
- Optimized Media Format / Render Cache Format - fastest codec on Win = DNxHR LB, on macos = ProRes LT/Proxy;
- Enable all checkboxes in this section to save performance the most;
- Cache files location - insert folder Cache made earlier;
- Gallery stills location - insert folder Gallery made earlier;
Save current settings as a preset: go to Presets tab in Project Settings, choose Save As.. After saving the preset, choose it with a right mouse click and choose Save As User Default Config.
Image Scaling
Mismatched resolution files = Scale full frame with crop, this setting greatly helps in conform process, if material was re-scaled before color correction.
Color Management
Broadcast Safe: turn ON to help monitor colors to be safe for TV broadcast.
- -20 - 120 - most lenient option
- 0 - 100 - most strict option
Check current colors in Color room go in menu View → Display Safe Broadcast Exceptions
Get the colors back to safe with either using HUE vs SAT instrument, or Gamut Mapping OpenFX plugin (Gamut mapping method = Saturation Compression, lower Saturation Max level).
Global Preferences
These preferences work for the whole system and all projects.
System - Memory & GPU
- Resolve Memory usage - give all available memory to DaVinci, if no games played or apps used same time as DaVinci;
- Fusion Memory Cache - needed for Fusion compositing rendering and playback in real time;
- GPU - leave Auto in case no problems. For macOS choose = Metal, for PC Intel/AMD card = OpenCL, for NVIDIA choose CUDA. GPU Selection Mode needed for several GPU cards on one computer: one can be used for interface, the other for rendering etc. Are 2 better than 1, should you connect both? Actually this depends on type of cards - does not give significant speed in notebook setup with external videocard, if both the external card and the inner card of the notebook are connected: this gives a few bonus seconds faster render but makes the notebook unusable during render process. Also inner notebook card gets connected to interface and previews, which makes them work slower.
- Create shortcuts for all folders actively used in the project;
System - Decode Options
Needed for work with RAW. Enable all checkboxes - for the GPU to use hardware Debayer on RAW material.
System - Audio Plugins
The folder containing 3rd party VST plugins for Fairlight, in case DaVinci did not find them itself.
User - Color
- Always perform copy and paste on selected nodes. Should be turned ON to do copy-pasting in DaVinci.
User - Project Save and Load
- Live Save checkbox. This makes DaVinci save any change, like FCPX;
- Configure Project backups: every 6 min, every 1 hour, every 1 day.
- Choose Backup location folder, created previously.
Annotations to video
Create anntations to video to future self or other artists:
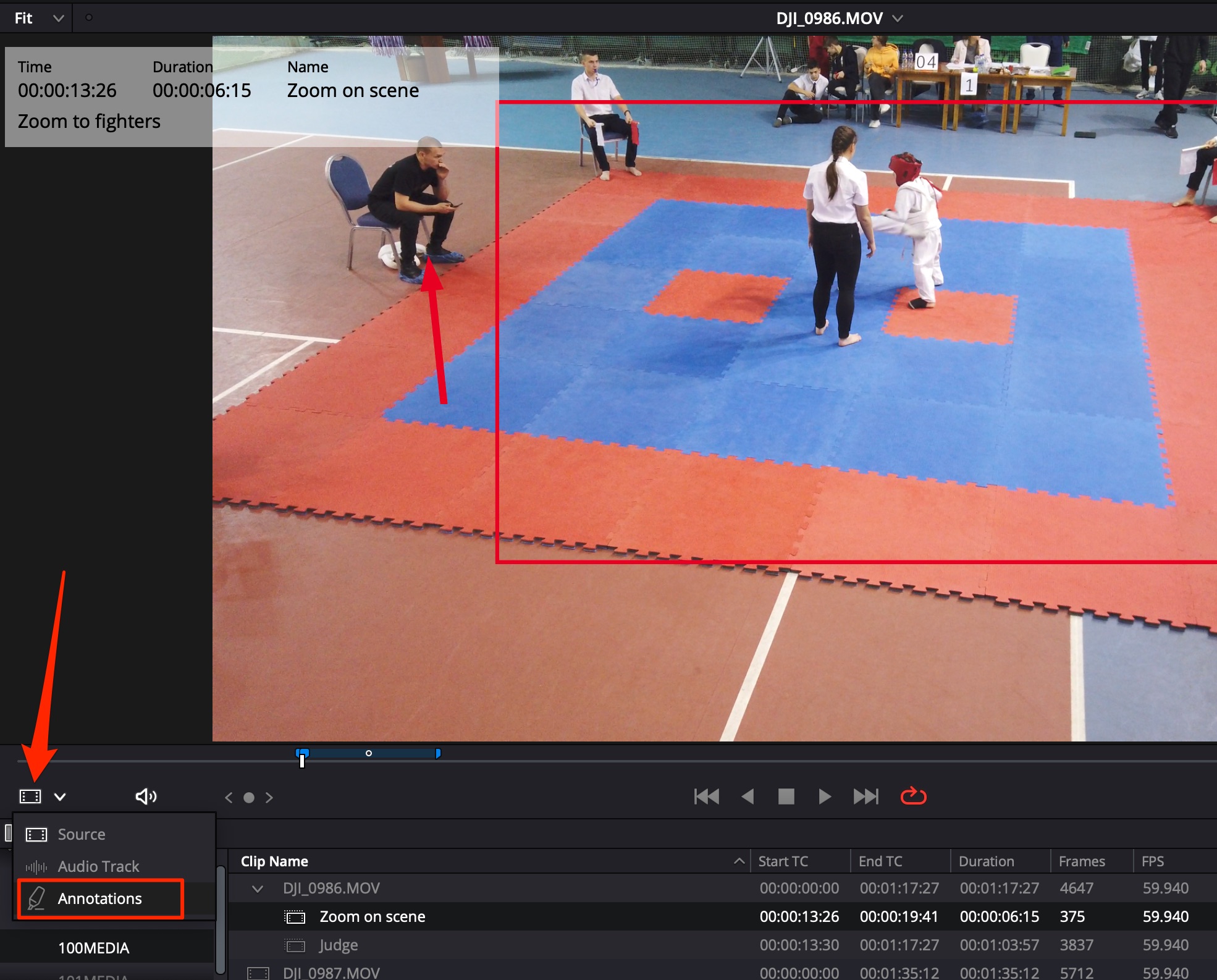

- Use M,M to label the created annotation markers;
- Use ALT+click on the marker to change its’ duration.
Annotations translate to every other room in DaVinci Resolve.
Use Proxy to optimize performance. Use column header Proxy to check if proxies were created for video.
In Color Room, turn off proxies to check color drift.
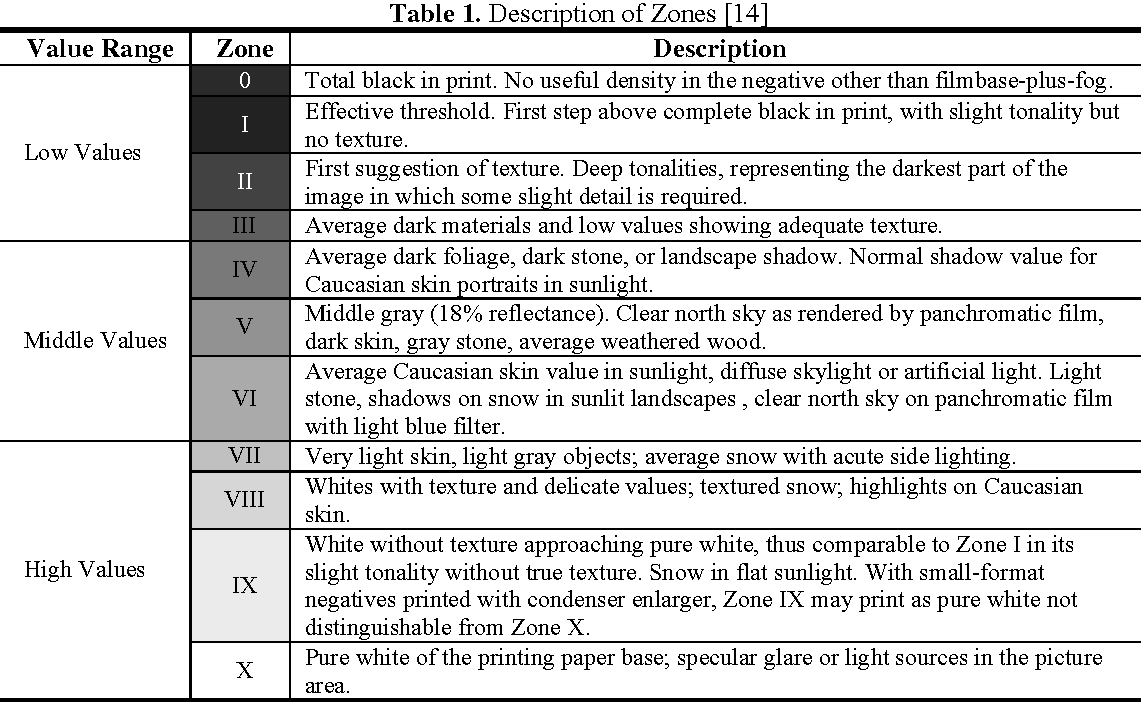
Exposure Guide in DVR
Use Ansel Adams Zone Model to divide exposure in 10 parts

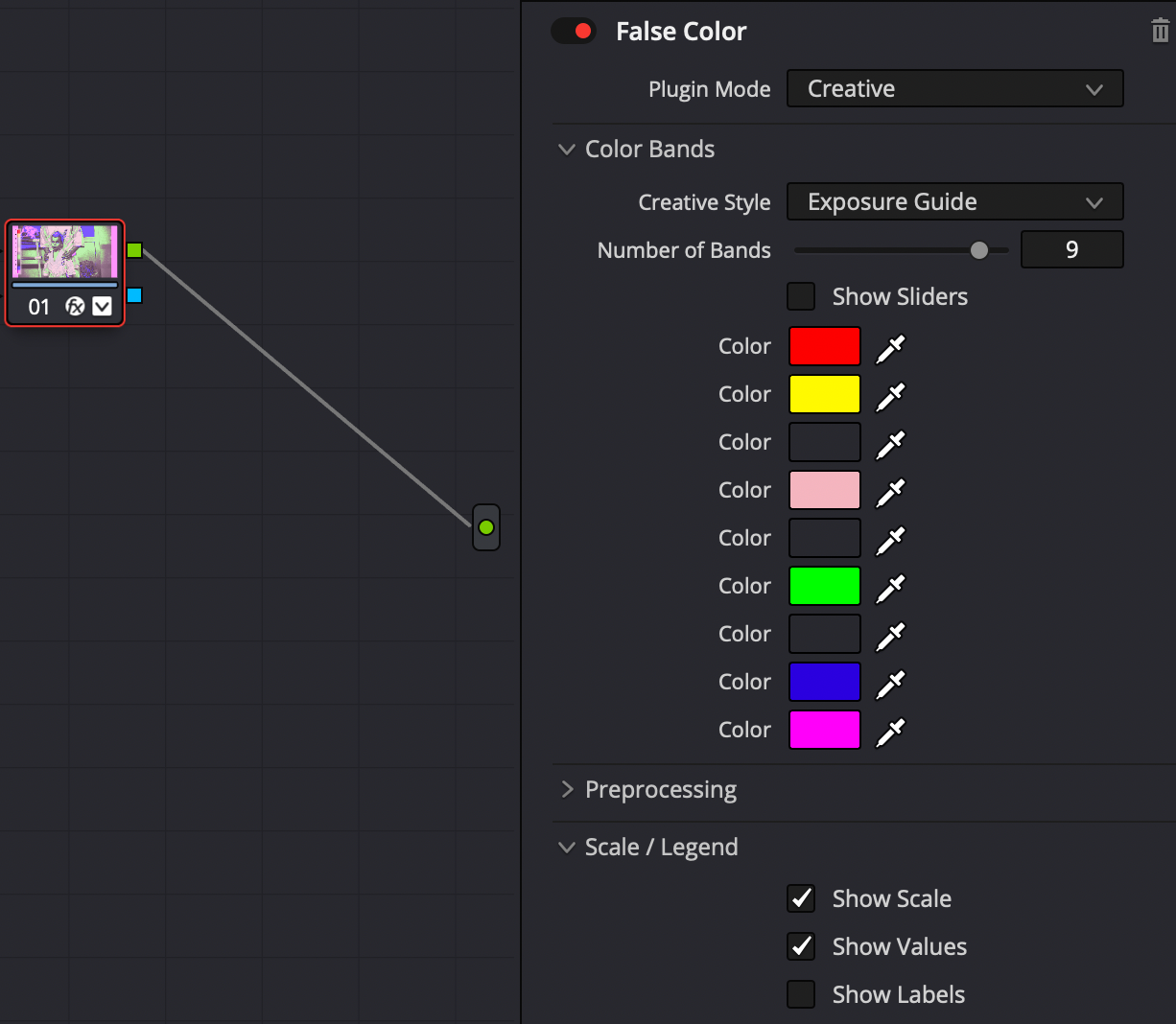
Check the video by using Effects -> False Colors.
Configure the effect: Plugin Mode = Creative, Creative Style = Exposure Guide

DVR Hotkeys
Global Keys
CTRL+Z - Undo
CTRL+SHIFT+Z - Redo
Rooms, Sections
- SHIFT+1 - Project Manager
- SHIFT+2 - Media
- SHIFT+3 - Cut
- SHIFT+4 - Edit
- SHIFT+5 - Fusion
- SHIFT+6 - Color
- SHIFT+7 - Fairlight
- SHIFT+8 - Deliver
- SHIFT+9 - Project Settings
EDIT TAB - Show/Hide Media Pool
EDIT SHIFT+TAB - Show/Hide Inspector
~ - Enter DaVinci Full Screen
ctrl+~ - See video from Preview in Full Screen (to switch betwwen clips use this from Color tab and ARROWUP/ARROWDOWN)
Playhead keys
- 1 - backwards
- 2 - pause/run
- 3 - forwards
- 4 - In Point
- 5 - Out Point
- 6 - Insert selected to timeline at playhead position
In/Out Points
EDIT X - create In/Out points around selected clip
EDIT ALT+X - delete In/Out points
EDIT SHIFT+A - create In/Out points around several selected clips
EDIT Q - Trim to playhead from left
Markers
EDIT M - Create marker (double-tap M,M - create maker & launch marker config window)
EDIT ALT+M - Delete selected marker
EDIT SHIFT+ARROWUP/ARROWDOWN - move playhead between markers
Editing Keys
EDIT W - Split on playhead
EDIT E - Trim to playhead from right
EDIT S - Ripple delete selected clip
EDIT D - Enable/disable clip
EDIT T - Trim edit mode tool
EDIT CTRL+D - Delete all gaps between selected clips
EDIT - ARROWUP/ARROWDOWN - Select prev/next clip in timeline
EDIT - ARROWLEFT/ARROWRIGHT - Move by 1 frame left/right
EDIT - SHIFT+ARROWLEFT/ARROWRIGHT - Move by 1 second left/right
EDIT - . / , - Move selected clip left/right by 1 frame
EDIT - - / = - Zoom Out/In timeline (Also ALT+SCROLLBUTTON or ALT+SCROLLTRACKPAD gesture), also SHIFT+W for Zoom In
EDIT CTRL+SCROLLTRACKPAD - scroll timeline (or CTRL+SCROLLBUTTON)
EDIT SHIFT+SCROLLTRACKPAD - scale in/out track on timeline (or SHIFT+SCROLLBUTTON)
EDIT - SHIFT+Z - Zoom to fit timeline
EDIT - ALT+ARROWUP/ARROWDOWN - bring selected clip up/down a track on timeline
EDIT - SHIFT+~ - Reveal Transform border over selected clip in viewer window
EDIT - CTRL+SHIFT+V (done after CTRL+C) - Paste selected attributes on selected clip / paste clip with no overwrite - moves adjacent clips to the right
EDIT - CTRL+SHIFT+X - Remove attributes from selected clip
EDIT - P - Open clip attributes windows
EDIT - F - turn snapping ON/OFF (also use N)
EDIT - ALT+F - find selected clip from timeline in Media Pool
EDIT - CTRL+SHIFT+F - find & show selected clip from Media Pool in Finder
Compound Clips
EDIT - CTRL+E - create a Compound clip from selected clips
EDIT - CTRL+SHIFT+E - enter inside Compound clip
EDIT - ALT+SHIFT+E - decompose a Compound clip
Clip Timeline Properties / Retime
EDIT - G - turn linked selection ON/OFF
EDIT - C - unlink/link video+audio of selected clip
EDIT - R - Open clip speed window (+Ripple timeline in config will move adjacent clips without overwirting them)
EDIT - SHIFT+R - clip speed overlay on selected clip
EDIT - CTRL+R** - clip speed menu for clip
EDIT - CTRL+SHIFT+R - show retime curve: ALT+click on curve to add speed points fast
EDIT - CTRL+ALT+R - reset retime controls to 100%
EDIT - SHIFT+C - Curve Editor on selected clip
EDIT - CTRL+SHIFT+C - Keyframe Editor on selected clip
EDIT - L - Loop mode ON/OFF
EDIT - SHIFT+SPACEBAR - play the loop (use In/Out points to define the loop interval)
Y - select clip & press to select all other clips to the right in the track from the current selected one
CTRL+Y - clip & press to select all other clips to the left in the track from the current selected one
EDIT H - show current Timeline you are working in at Media Pool
Room - Fusion
Articles in section
Fusion Settings
Menu Fusion → Turn OFF Show Toolbar;
Menu Fusion → Fusion Settings…
- General tab: Proxy → Standard change to 4:1;
- Flow tab: Source Tile Pictures=ON will show video thumbnails in node graph instead of plain rectangles;
- Flow tab: Arrange to Connected=ON helps organize connected nodes;
- Flow tab: Show grid=OFF lessens visual garbage on Node graph;
- Flow tab: Build direction=Vertical to streamline node creation with software such as The Foundry Nuke or SideFX Houdini;
- Frame format tab: Lock depths=16bit float per channel(64 bit) will significantly enhance inner image processing quality;
- User interface tab: Zoom Cmd=OFF, Pan Cmd=ON - this will enable zoom with simple mouse wheel like in many other editors.
Note
Reboot of DaVinci Resolve needed after settings saved.
Hotkeys in Node Graph
SHIFT+SPACE - search&create node by name menu
CTRL+T - switch inputs (in merge node switch background & foreground)
Connecting output of one node to the output of another node will automatically create a Merge node;
Tips
Editing Color Curves color correction and other nodes splines in Spline Editor
- Put a Color Curves node;
- Open Spline Editor. In its’ menu …, choose Show only Selected Tool, then click Zoom to Fit button (diagonal arrows in a square).
Copy perspective view to camera view
- Connect camera node to Merge node;
- While Merge node is selected in graph, in perspective windows rotate the view, the Mouse Right-Click → Camera → Copy PoV To → Choose the connected camera.
Reactor Plugin Manager
Link: https://www.steakunderwater.com/wesuckless/viewtopic.php?f=32&t=3067
- Drag & Drop the Reactor LUA script into Fusion nodes field, install;
- Check out Reactor in Workspace → Scripts → Reactor → Open Reactor…
To remove plugins from Reactor, use Remove button. Do not un-tick them.
Handy plugins
- xGlow - advanced version of Glow node;
- FastExpoGlow - gives a golden light;
- HeatDistortion - hot air effect.
Subsections of Room - Fusion
Masks
Diagonal Crop
Use Polygon mask in Fusion to create a diagonal crop, with underlying video creatively seen.
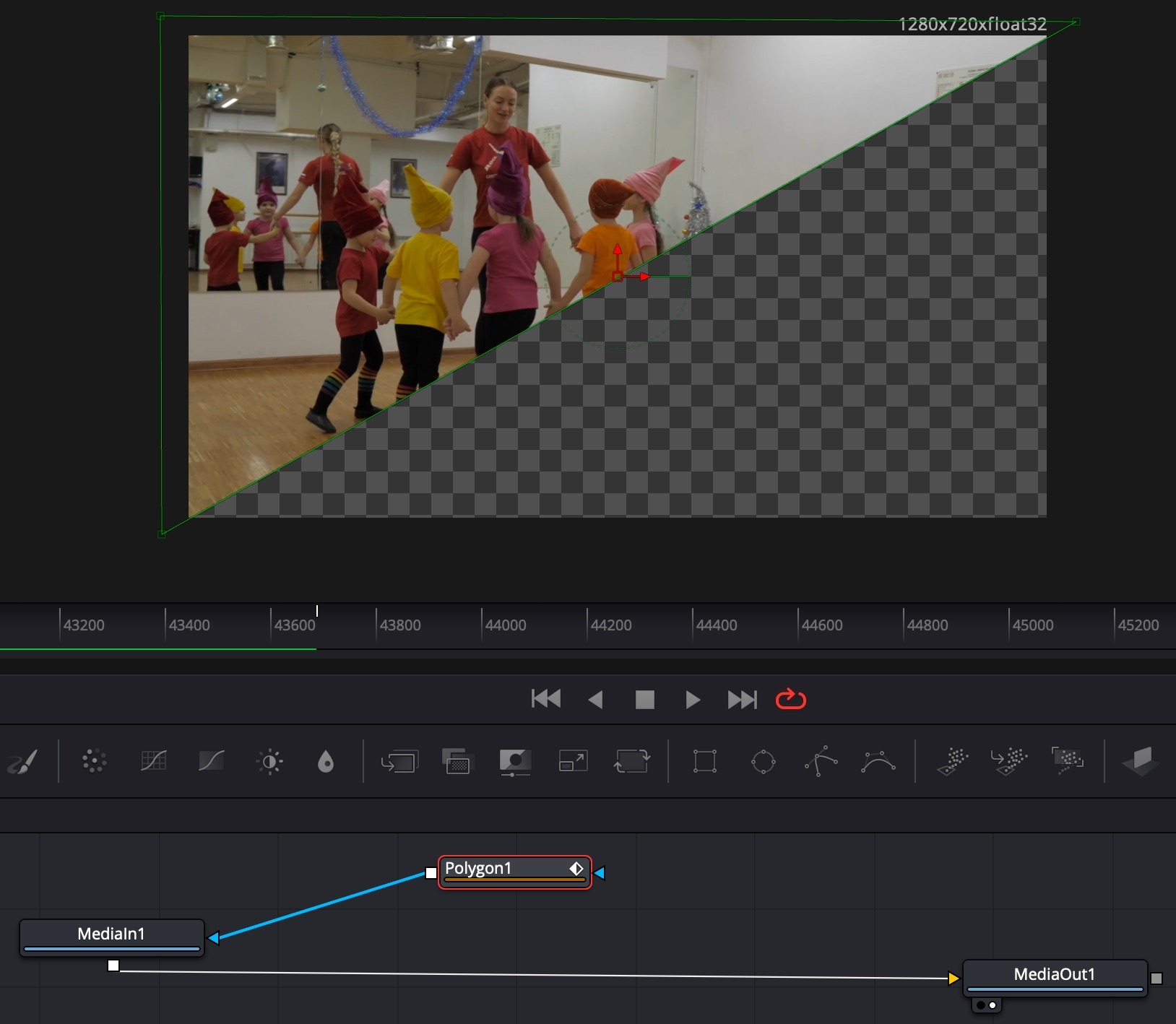

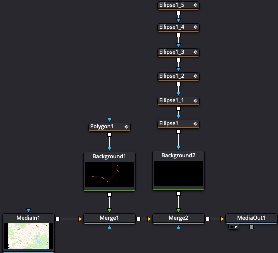
Travel Maps
External Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Vb42fYP6FBU
- Choose a large map picture, throw it in DaVinci Resolve Timeline;
- Make the still image video 10 seconds in length;
- Open the map image video in Fusion Room;
- Add a Background node and Merge it with the MediaIn node;
- Add a Polygon node and connect it to Background node;
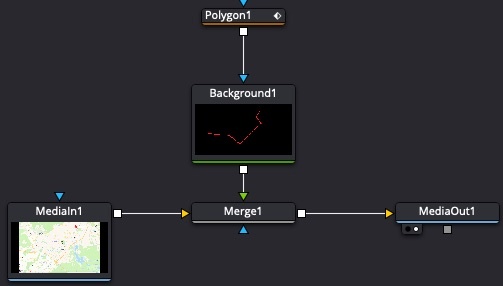

-
Choose the Polygon node, then in the Viewer draw line segments from point A to B;
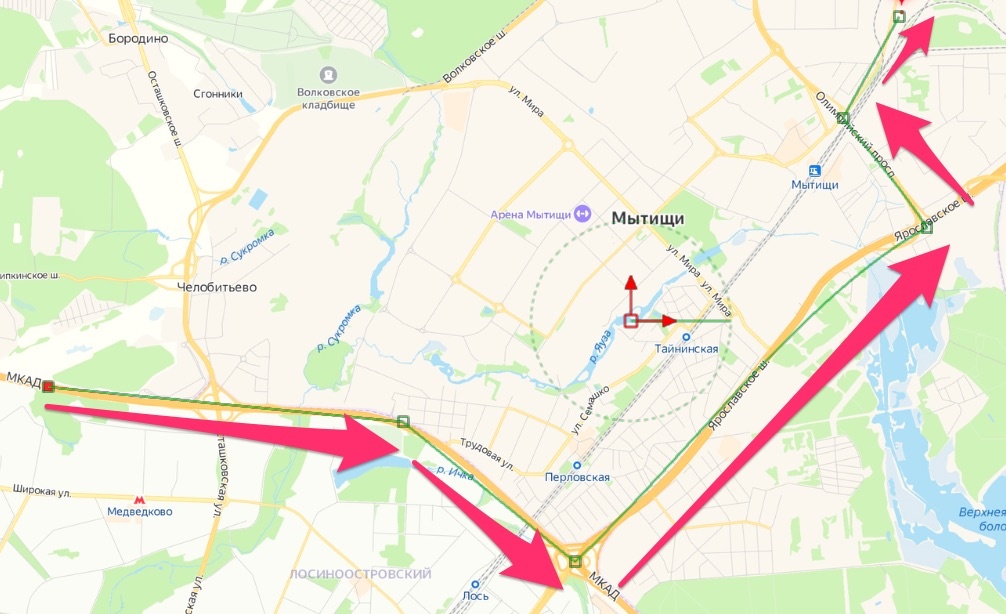

-
In Polygon node → Controls → Border Width = 0.006 add border width to see the line. Choose Polygon → Controls → Border Style to make line ends round or square;
-
Change Background node Background → Color to make the line colored appropriately;
-
Animate the Polygon node → Controls → Length from 0 and frame 0 to 1.0 at last frame;
-
In Spline Editor choose both keyframes, make them smooth (hotkey S). Then use hotkey T to select Ease In = 45 and Ease Out = 35;
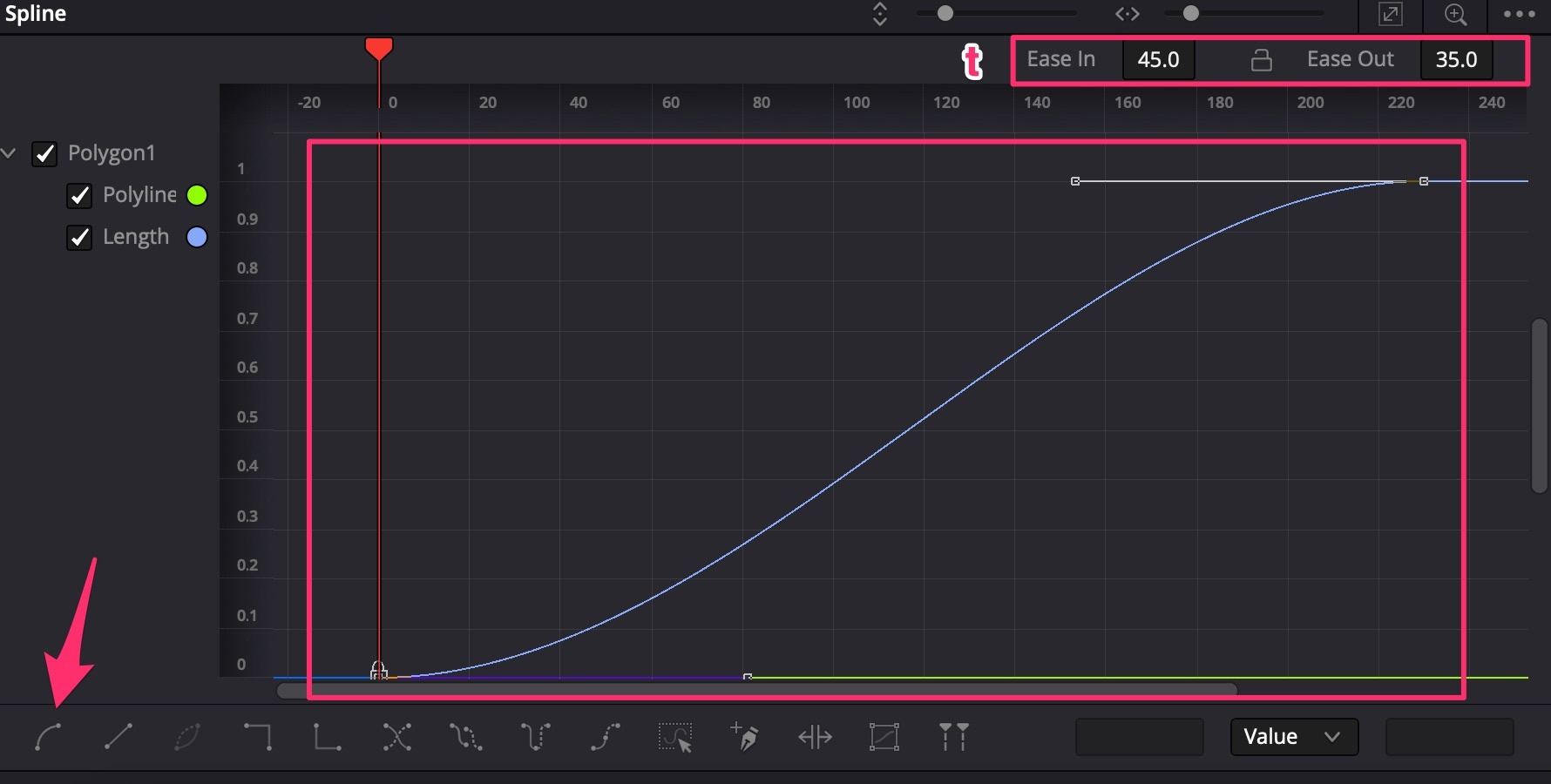

-
Create map points: add a new Background node, Merge it with the previous Merge node;
-
Add an Ellipse node, drag the border of the ellipse to make it a small point;
-
Animate Ellipse → Controls → Border Width from small negative number to 0 to make the point pop out when travel line starts from it;
-
Go to Spline Editor, choose the Ellipse keyframes and press S to make them smooth;
-
Ctrl+C copy the Ellipse, then Ctrl+V paste it to make other points for the travel line. Move them to appropriate positions;
-
Use the Keyframes editor to move the keyframes of ellipse copies in the appropriate frames of time.


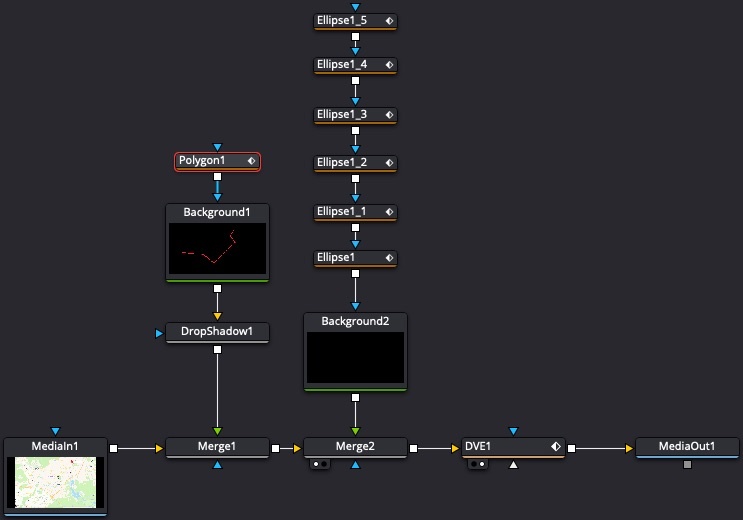
Make Pseudo-3D Effects
- Add Drop Shadow node, connect it after the Polygon + Background nodes, before the Merge node;
- Reduce Drop Shadow → Controls → Blur parameter, reduce the Drop Shadow → Controls → Drop Distance parameter to make the shadow closer;
- Add the DVE node just before MediaOut node;
- Adjust DVE → Controls → Z Move = 0.3. Adjust DVE → Controls → Rotation → X and Y to make cool 3D-like effect;
- Make the Viewer into Dual-View, and put result of DVE in one viewer and Merge node before it in second Viewer windows;
- Adjust DVE → Controls → Pivot → X slightly to see the large X in the viewers. Grab the X and move it to the first point of the line;
- Animate the Pivot by dragging it to points following the travel line. The use the Spline editor to choose all keyframes and make the animation smooth (S);
- Go to Polygon node and edit Polygon → Settings → Motion Blur = ON, Quality = 9.

Room - Deliver
General Web Export
Preset = H.264
Quality restrict to:
- 10000 - 40000 Kb/s - for 1080p
- 20000 - 80000 Kb/s - for 4K UHD/DCI
- 6000 - 9000 Kb/s - for Instagram, 720p. More is not needed since video will be re-encoded by their codec.
For RAW footage:
- Force sizing to highest quality
- Force debayer to highest quality
Room - Color
Articles in section
Color Room Hotkeys
General
- SHIFT+D - Grade Bypass (Disable). Disable all nodes to see the original image;
- CTRL+D - Grade Bypass (Disable) on current node;
- SHIFT+H - see node mask, or qualifier mask etc. in monitor windows;
- CTRL+F - See preview window in Full screen.
Create nodes
- ALT+S - New Corrector (Serial) AFTER selected node;
- SHIFT+S - New Corrector (Serial) BEFORE selected node;
- ALT+L - Add Layer lower than current node;
- ALT+O - New Outside node (Includes everything NOT selected in previous node)
- ALT+P - New Parallel node.
Tracker
- CTRL+T - Track mask forward;
- ALT+T - Track mask backward.
Versions
- CTRL+Y - add new color grade version;
- CTRL+N - switch to next version;
- CTRL+B - switch to previous version.
PowerGrades
Create a PowerGrade folder to store color grading across all projects.
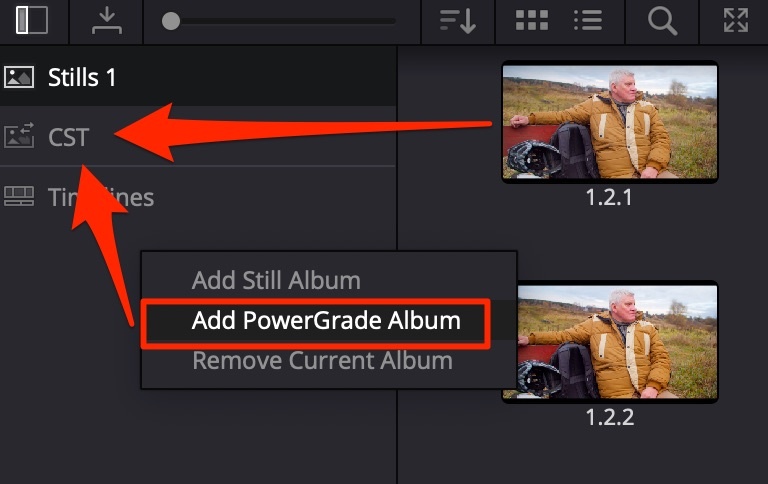

Captured stills can be put into this folder → go into the DaVinci Database and are shared across all projects. A convenient way to store ready-made Color Space Transforms for different camera colorspace/gamma types. Use Append Node Graph to apply the grade, do NOT use Apply Grade since this changes the original ISO of the footage, which may differ in the specific scene.
Tracker
Cloud tracker - tracks using a whole mask with all its’ points.
Point tracker - needs control points on contrast areas, which it uses to track.
Stills
Right-click on footage → Grab Still: this saves the footage with currently applied grade. After any changes to the image, you can find the still in Gallery, and:
- double-click on still to make a A|B compare picture. CTRL+W to see changes on full screen (disable still);
- right-click → Apply Grade to apply to what was saved. Stills can be applied to any footage to copy correction or try interesting results.
Subsections of Room - Color
Color Balance
Tip to help reach ideal neutral color balance.
- Create Serial Node for color balance correction and 2 Layer nodes;
- Apply OpenFX module Color Generator to second Layer Node;
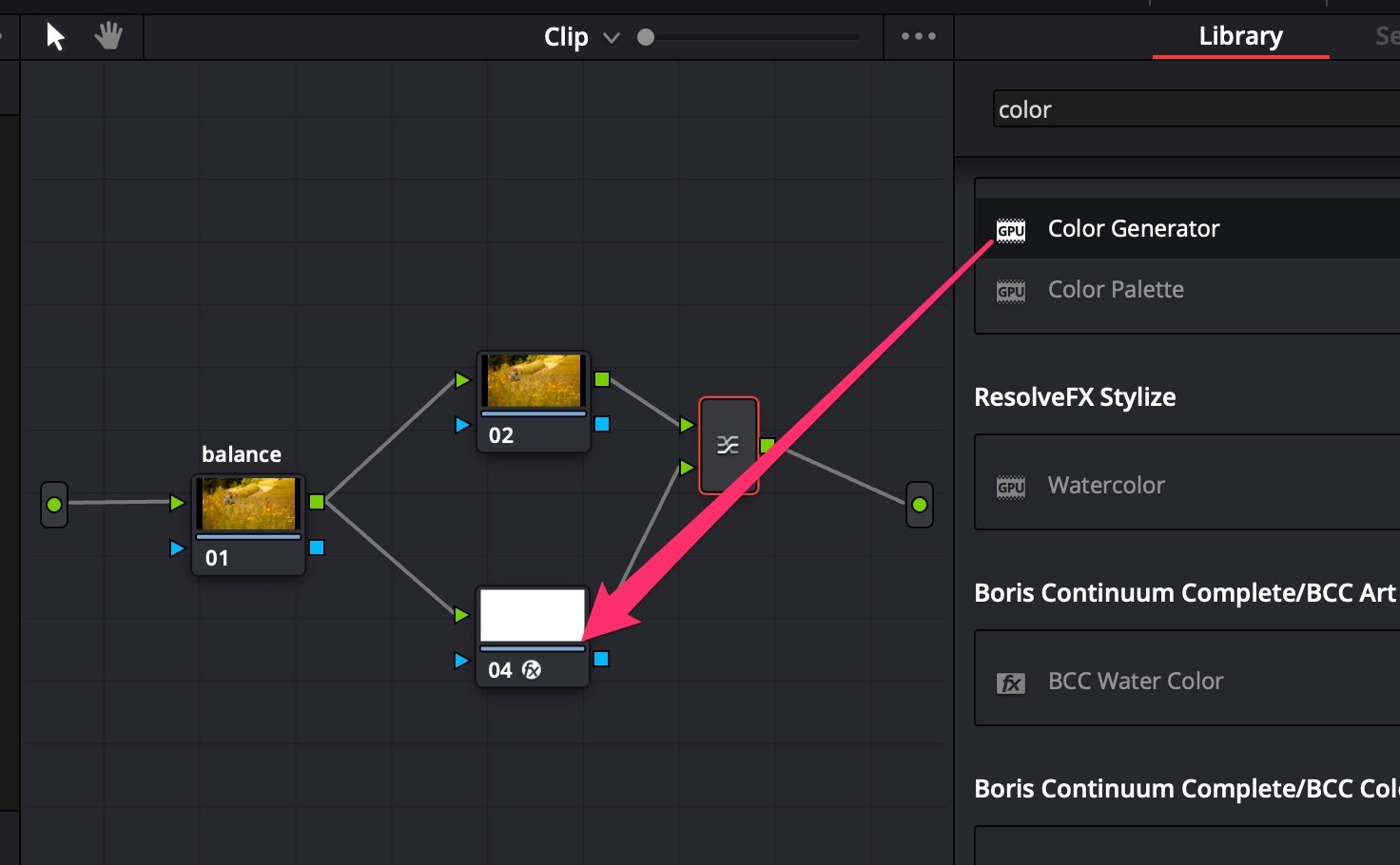

- In Color Generator options choose Color = HEX #808080 (neutral gray);
- Choose Composite Mode = Luminosity;
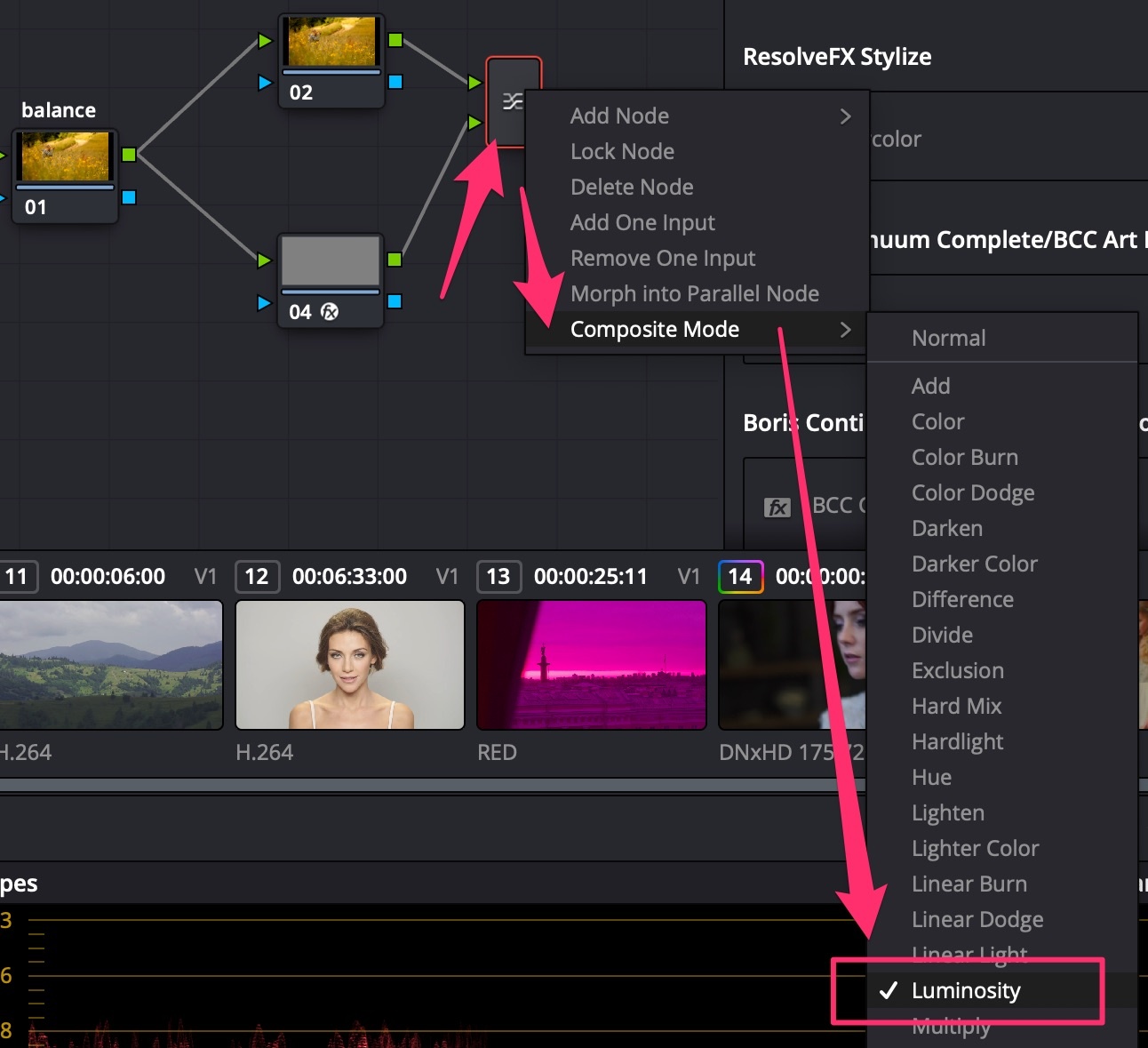

- In balance Serial Node, add +Saturation to see color offset;
- Turn on Scopes = Parade;
- Use Offset Wheel to neutralize colors (Parade RGB levels equal);
- Turn OFF the layer node with color generator.
Color Grading
Scenarios
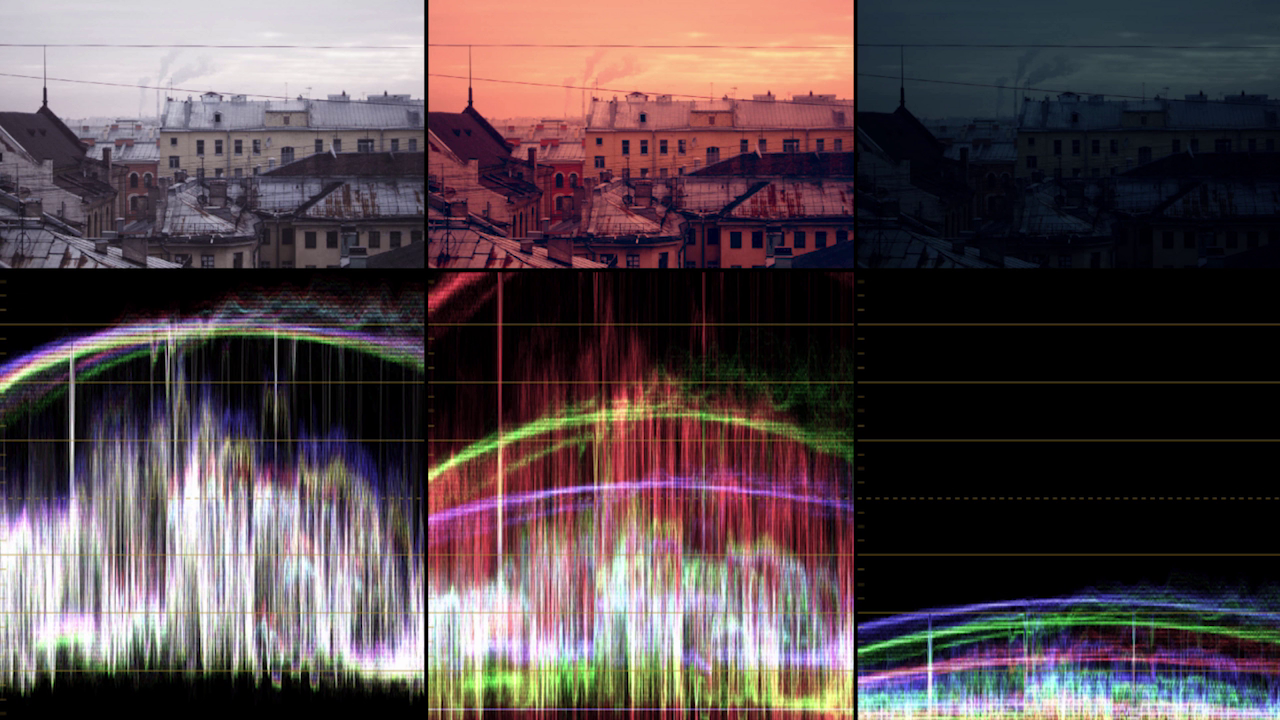
Свет в городском пейзаже
- Закат - много красного, оранжевого в средних и в светлых тонах, синий цвет в тенях противопоставляется;
- Рассвет - более холодный чем закат, больше зелёного чем красного/оранжевого;
- Ночь - в кино обычно синяя ночь, чем чёрная. Небо сохраняет светлость;
- Унылый серый город - снизить насыщенность (Saturation), чтобы это подчеркнуть.

Цвет в портрете
Хакрактер рисуется контрастом. Обычно грейдинг начинается с опусканием вниз теней. Дальше отделение от фона.
Работа с ЧБ портретом
Человек не воспринимает ЧБ как именно ЧБ, он ищет и выдумывает немного цвета. Поэтому ЧБ не делают полностью лишённым цвета, его чуть-чуть подкрашивают для придания настроения: для тёплого настроения подкрашивают в коричневый, для “глянцево-журнального” настроения - в синий. Количество подкраса совсем маленькое, совсем чуть-чуть, как петрушка в супе.
Teal & Orange
-
Start by grading the image into nice blue using all color wheels (Lift, Gamma, Gain), and distribute the wheels in a clockwise fashion between each other!
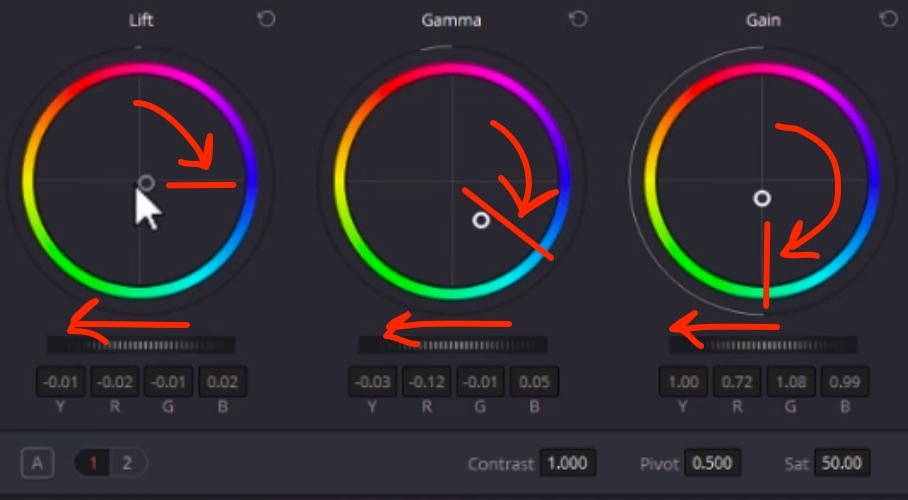

-
All colors in the image turn blue, but shadows have to stay neutral: user the Log wheels to fine tune: Shadow, Midtone, Highlight wheels between Low Range (default lower than 33% = shadows) and High Range (default higher than 66% = highlights). Turn the Shadow wheel to blue counterpart to make shadows neutral. Lower the Low Range (around 10%) so that midtones are not affected;
-
THEN mask out skin and other “warm elements” in the picture (in parallel node) and grade them into the opposite color - yellow-orange;
-
Use the Log wheels to balance the colors: make a soft bridge between warm skin and cold background by turning Shadow wheel to green a bit, Highlight to magenta;
-
Balance the footage colors, so the color work together, and not appear as isolated elements: one cheater method to do this is to radically darken the background. Since with teal&orange we get the maximum color contrast, it is better to make the light contrast stronger as well. Another method is to make subtle changes - bring the overcolored ares back by lowering saturation, for example.
Color Wheels → Color Boost (number in the below section) - increases/decreases the saturation of the MOST SATURATED colors in the image. Helps if you have some over-saturated colors which you want to level down, without touching the rest if the image.
Add Saturation to high values, then subtract Color Boost to remove color spills.
Example: vegetables in a white glass bowl will pass their color to the bowl. To keep it white, subtract Color Boost.
Цветокоррекция и покрас плёночного кино
В плёночном кино грейдинг являлся этапом PRE-Production. Это связано с необходимостью подбора правильной плёнки, дающей нужную гамму цветов. Для проявки плёнки проявочные машины (пример - российская машина МПМ—16—3М), которые работали по заданному СТАНДАРТУ.


Color Management
Videocard sends a signal to the monitor, divided in 2 components: COLORSPACE (color) and GAMMA (light)
COLORSPACE
Initial colorspace is a triangle-like model of all colors which are discriminated by the human eye (mathematical model):
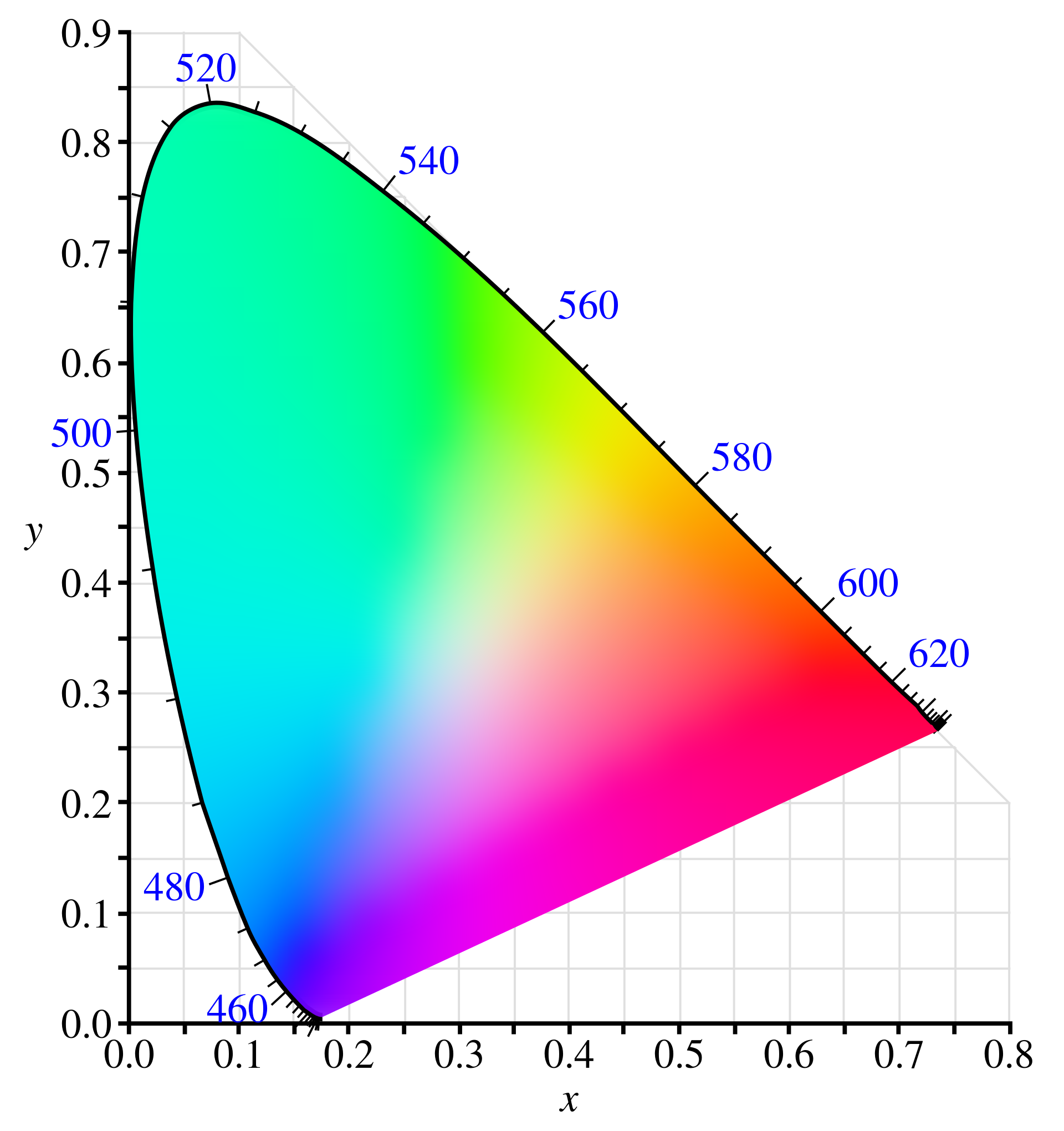
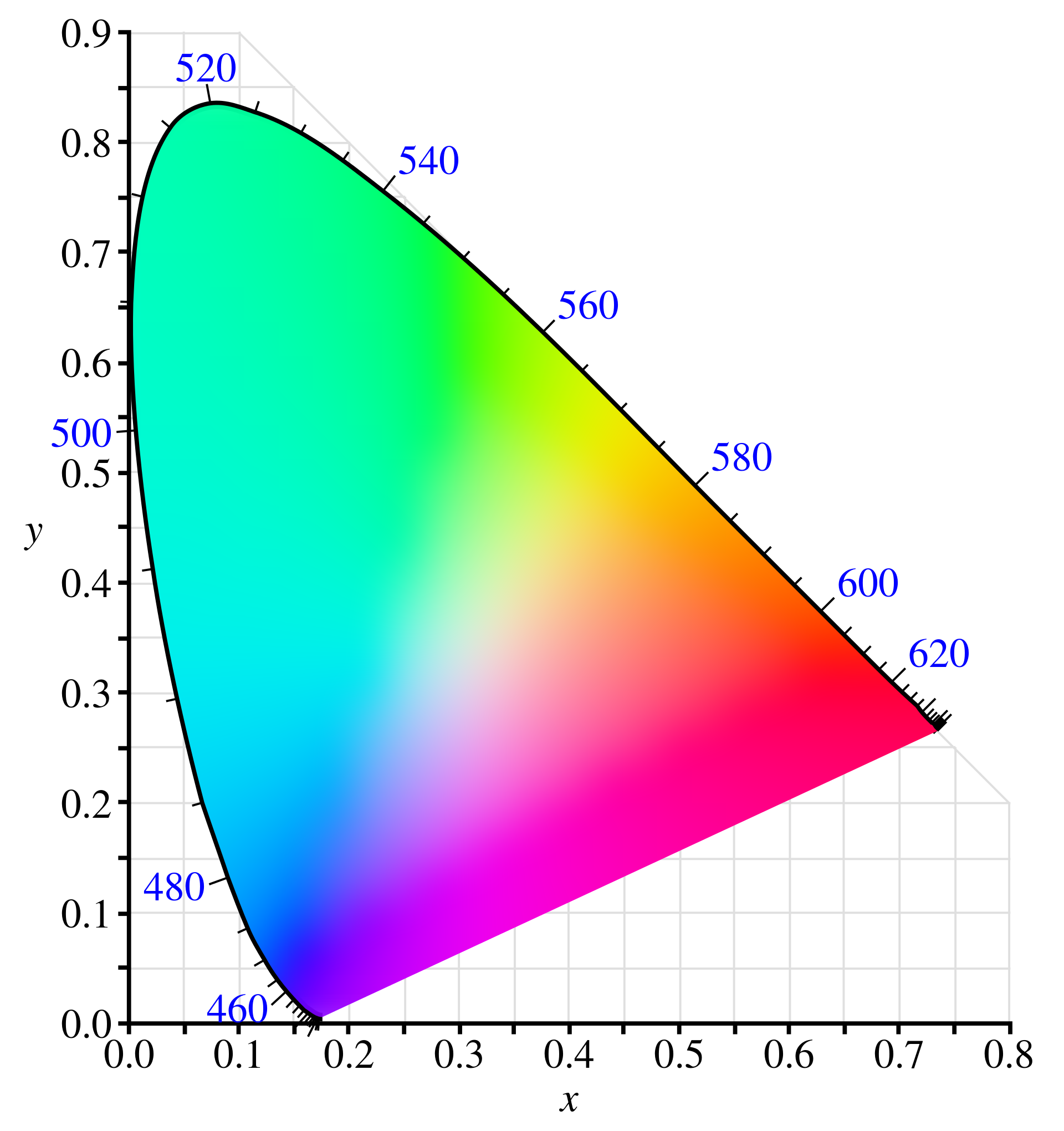 Different color spaces encompass different sets of colors as compared to this model:
Different color spaces encompass different sets of colors as compared to this model:
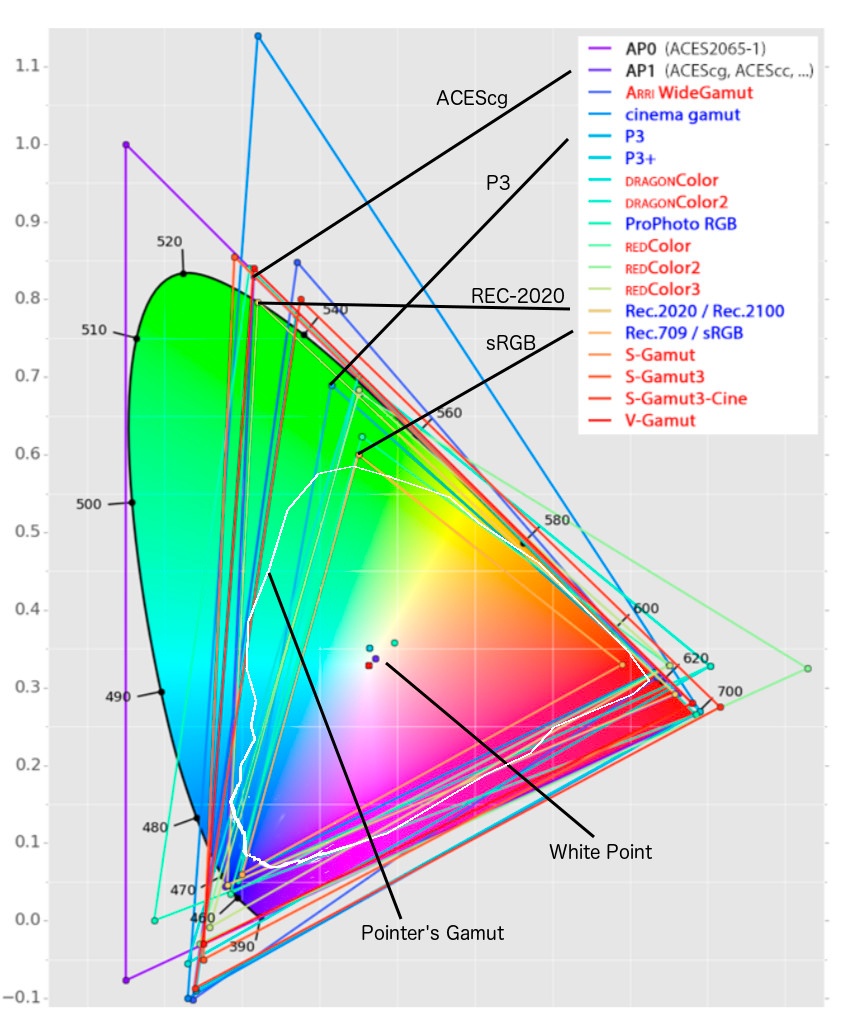
 rec709 - came with digital TV, P3 - used for digital cinema theater, rec2020 - UHDTV / new 4K video standard.
rec709 - came with digital TV, P3 - used for digital cinema theater, rec2020 - UHDTV / new 4K video standard.
GAMMA (Dynamic Range)
Digital cameras see the world in a linear fashion. If we have a room with 1 lamp and we bring in a second lamp, camera will register 2x increase of light. Human eye will register around +20% increase of light.
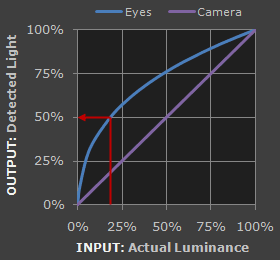
 Transfer function - math function to compress the light data of an image and then use this file to restore the whole dynamic range seen by the human eye.
Transfer function - math function to compress the light data of an image and then use this file to restore the whole dynamic range seen by the human eye.
- Human eye dynamic range: 10-13 stops active range, 24 stops total range
- Film dynamic range: 13 stops
- RED Weapon Camera: 16.5+ (incl HDRX-mode) stops
- HLG: 12 stops
- REC709: 6 stops
REC709 GAMMA 2.4 is the native format for DaVinci Resolve, Adobe Premiere etc. If you throw a different colorspace file in DaVinci, you must tell it what it is and convert: Color room → Library → ResolveFX Color → Color Space Transform.
Fir SONY SLog3 shoot with +2 or +3 F-stops higher to quell noise, then choose:
- Input Colorspace = Sony S-Gamut3
- Input Gamma = Sony S-Log3
- Output Colorspace = Rec709
- Output Gamma = Rec709
- Tonemapping = Luminance Mapping
Color Masks
Using Masks for Correction
Always use the curved mask: it is the only one that has soft transitions, which can be changed individually for different sides:
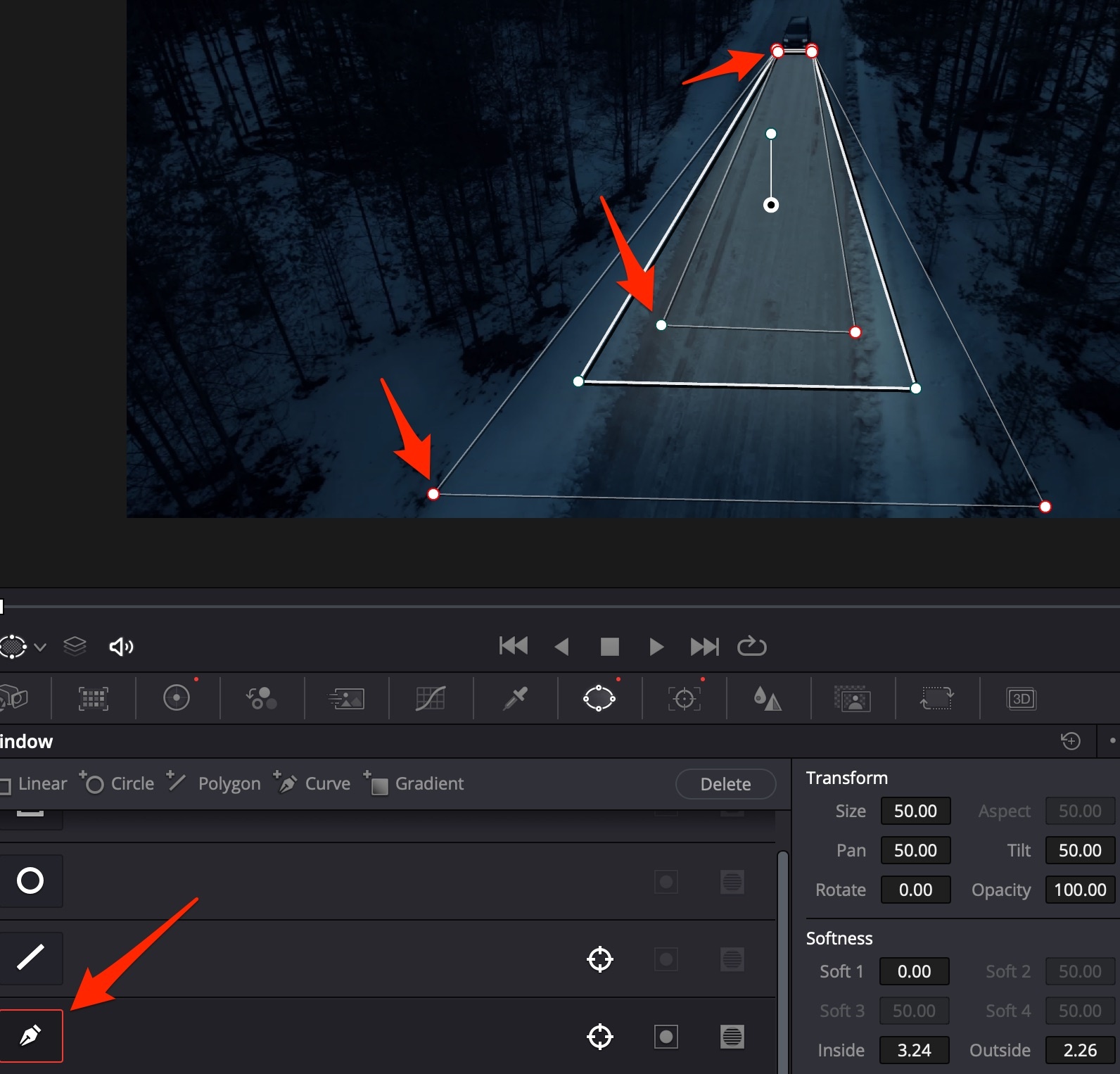

Neural Masks
Davinci Resolve Studio 18+ brings Object Mask to select parts of a person.
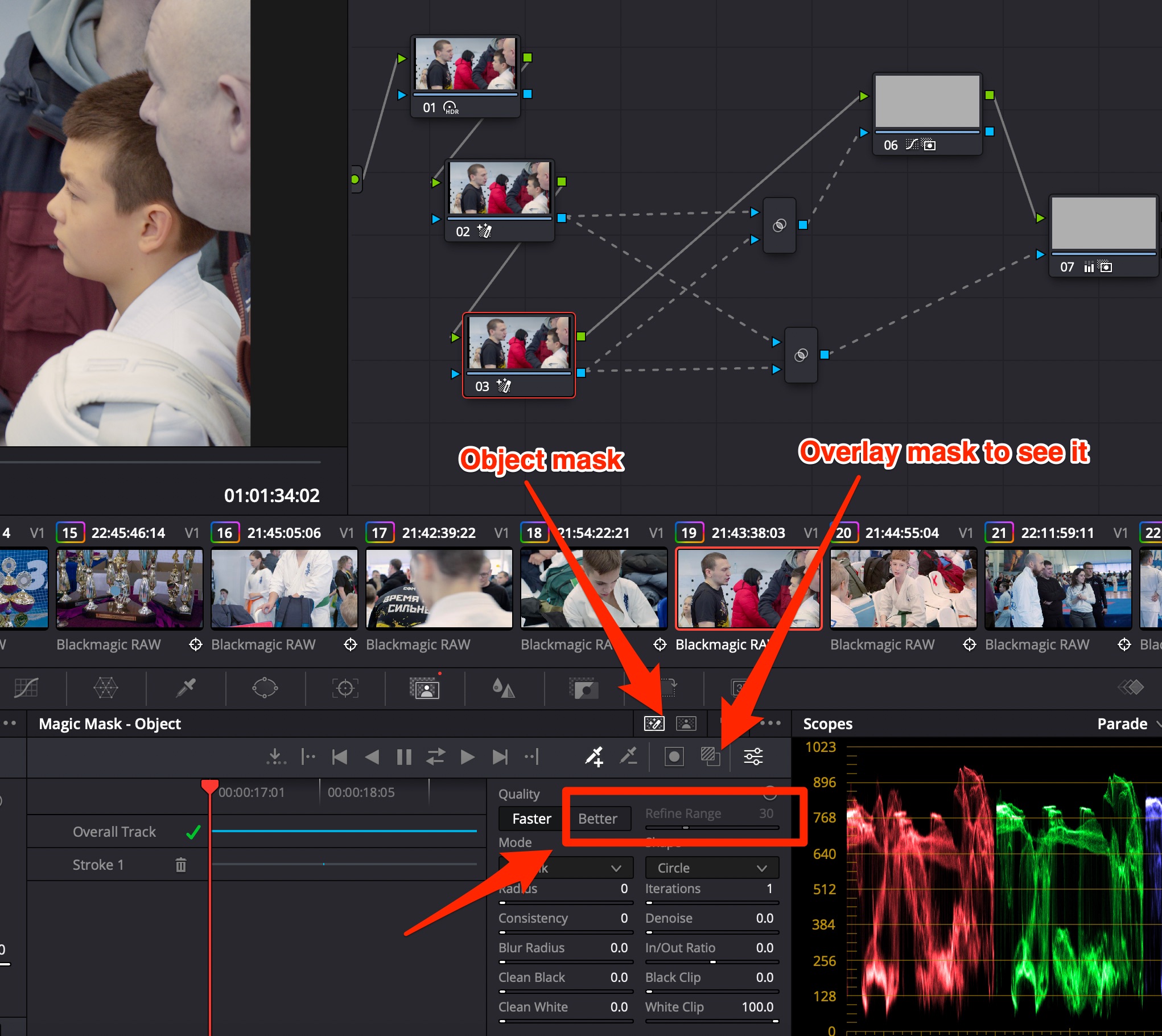
 Draw lines with dropper+ over face & other parts of a person to highlight them. Use dropper- to leave other objects out of the mask. Use Better quality with Refine Edge BEFORE calculating the mask.
Draw lines with dropper+ over face & other parts of a person to highlight them. Use dropper- to leave other objects out of the mask. Use Better quality with Refine Edge BEFORE calculating the mask.
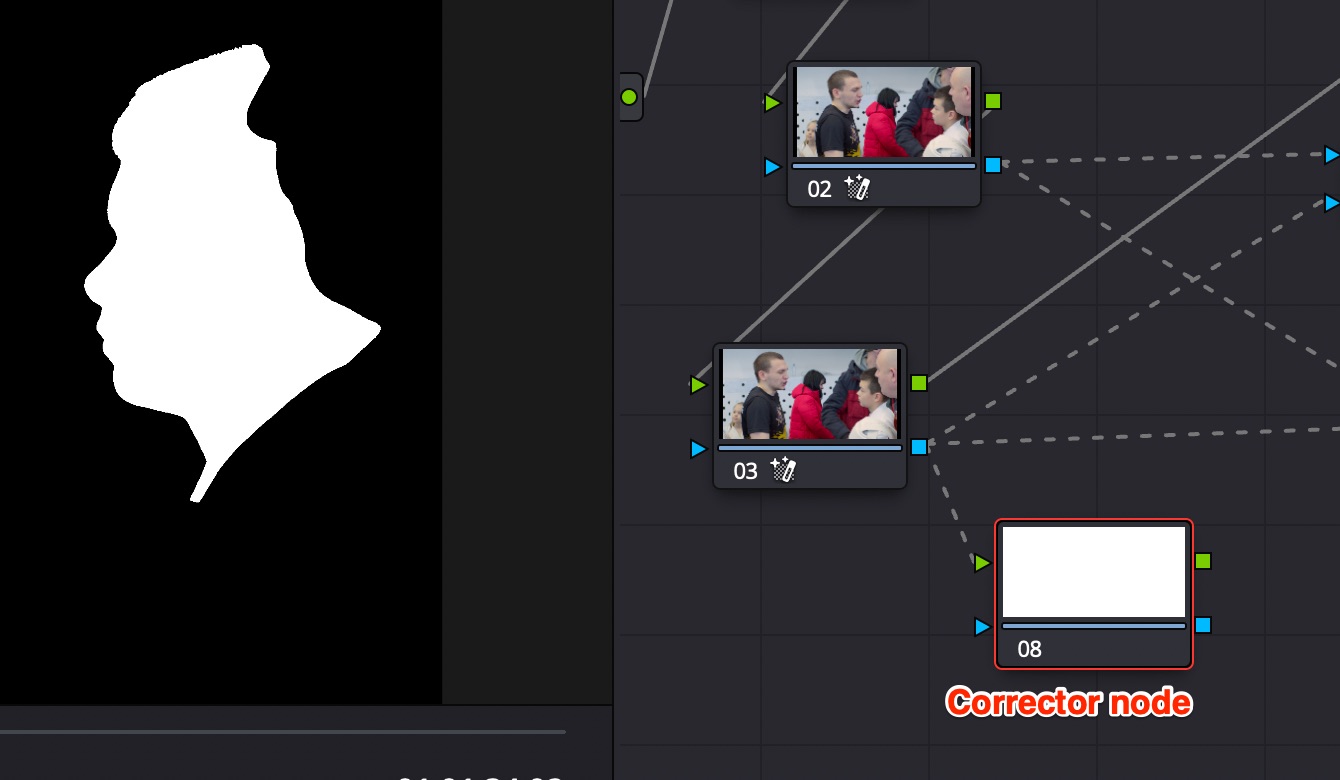
You can see the mask using Corrector node.

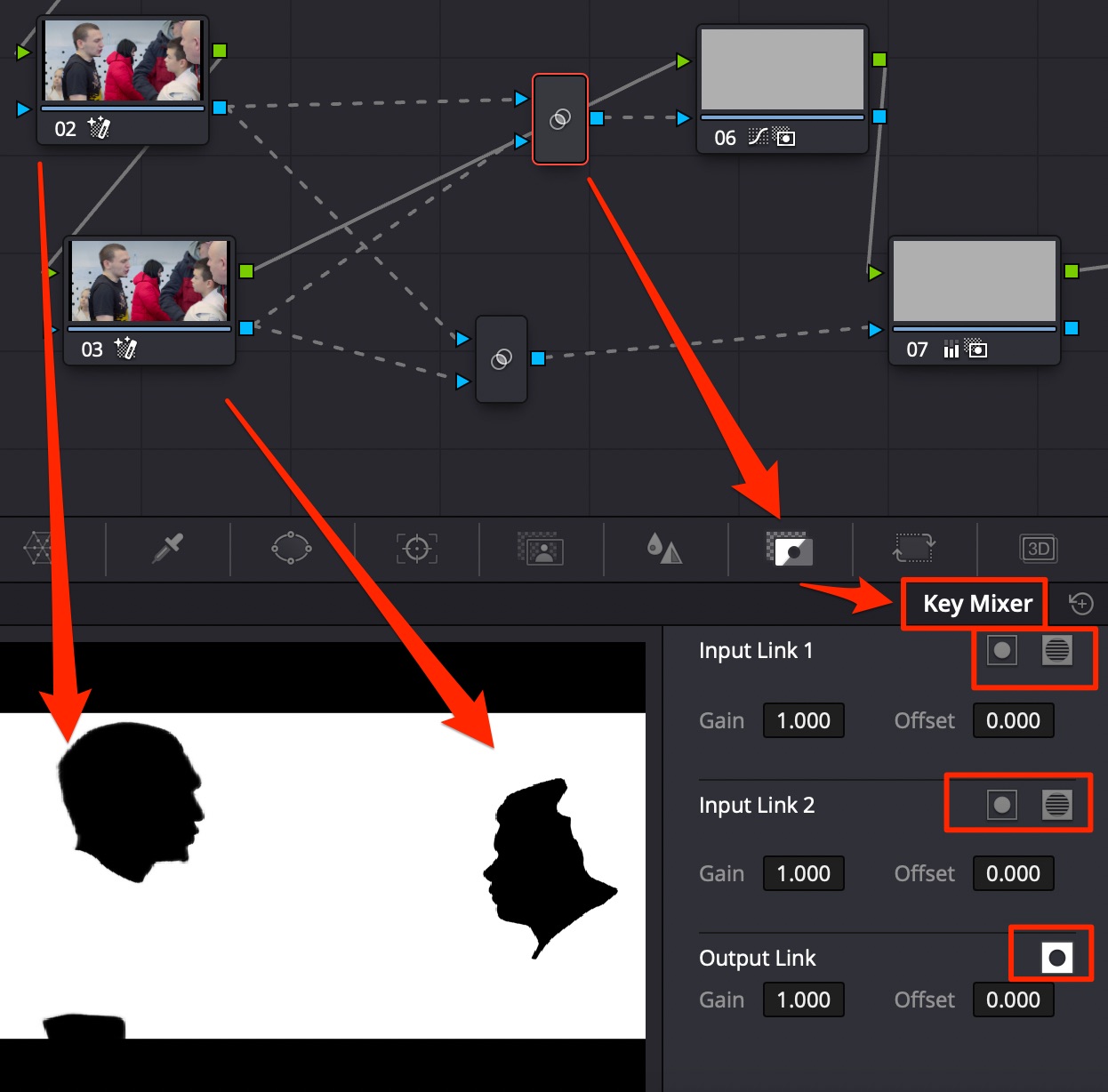
Use Key Mixer node to combine several masks (you can input more than 2, links are added in Key Mixer node automatically upon connection), invert them using button in Key Mixer config.

De-Noiser
Noise
Most of the noise is in red channel. Use DaVinci Resolve Studion version with 2 types of de-noise.
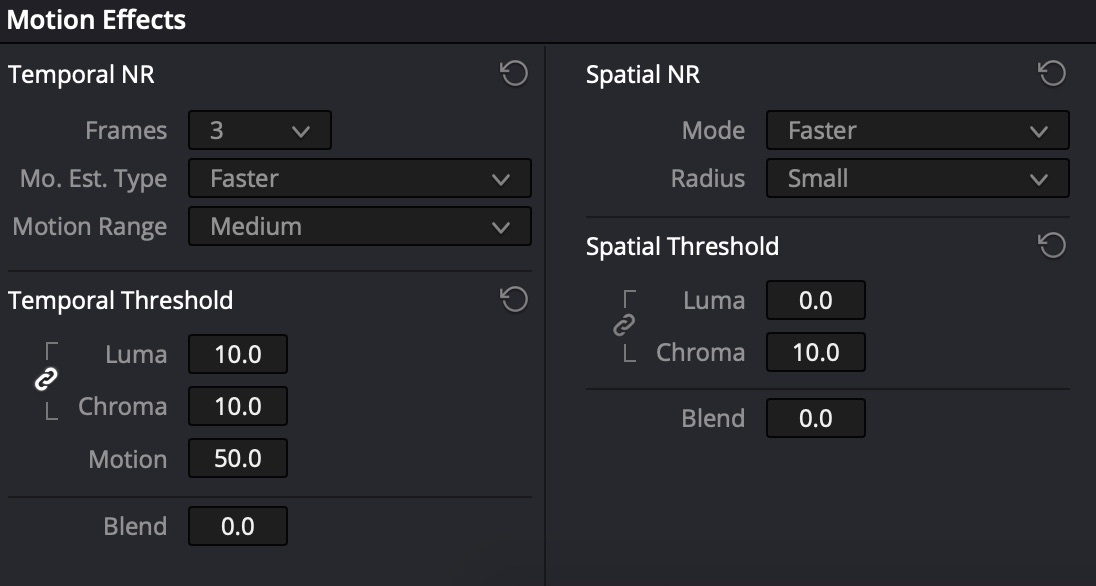

Motion Effects → Temporal NR
- In case of light noise: Frames=3, Mo. Est. Type=Faster, Luma=Chroma=~10+
- In case of heavy noise: Frames=5, Mo. Est. Type=Better, Luma=Chroma=~20+
Motion Effects → Spatial NR
Unlock Chroma != Luma. Raise Chroma=6-7
Moire
Moire on buildings and other landscape objects is countered by motion blur.
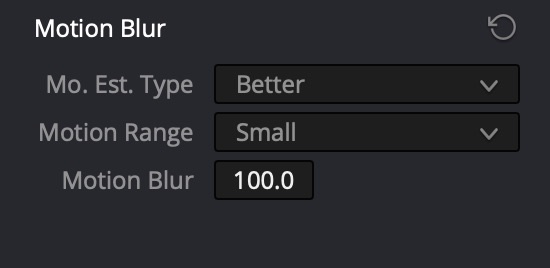

Motion Effects → Motion Blur
Mo. Est. Type: Better, Motion Range=Small, Motion Blur=100 (maximum).
Highlights
Blown Highlights
They can be restored using several methods:
- Use the wheels: lower Gain, then create node and restore contrast;
- Use the Curves: lower the curve in the highlight area, make “S” form to restore contrast;
- In the Curves instrument, use Soft Clip section: Low / High restores shadows / highlighs, while Low Soft / High Soft makes a smooth transition - ideal for blown sky areas.
Controlled Restoring of Blown Highlights
- Create a Parallel Node after the input together with the denoise node
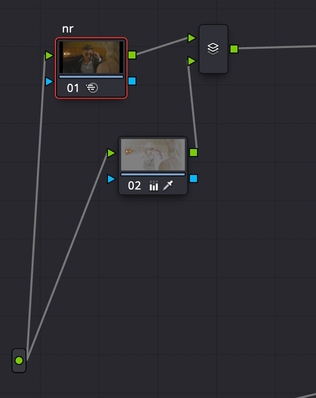

- Use Luminance Qualifier to select smoothly the bright part of the image;
- Turn down Highlights to get the details back.
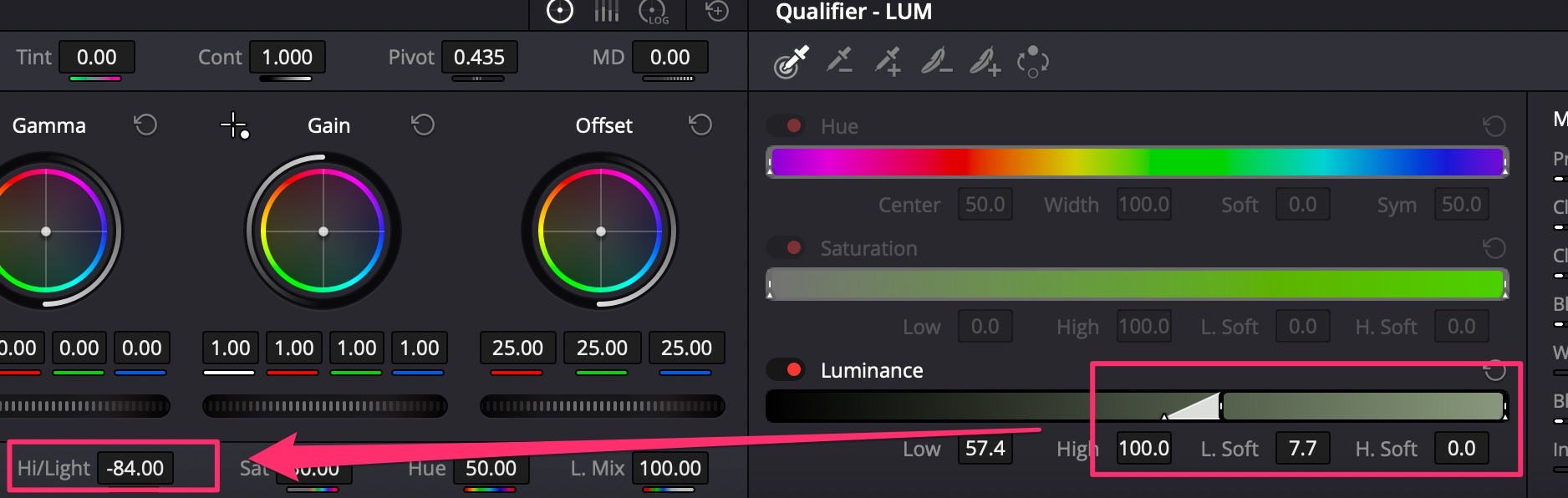

Parasite color in highlights
Typically such things appear when shooting on 8bit cameras. Use Lum Vs Sat Curve to fix.
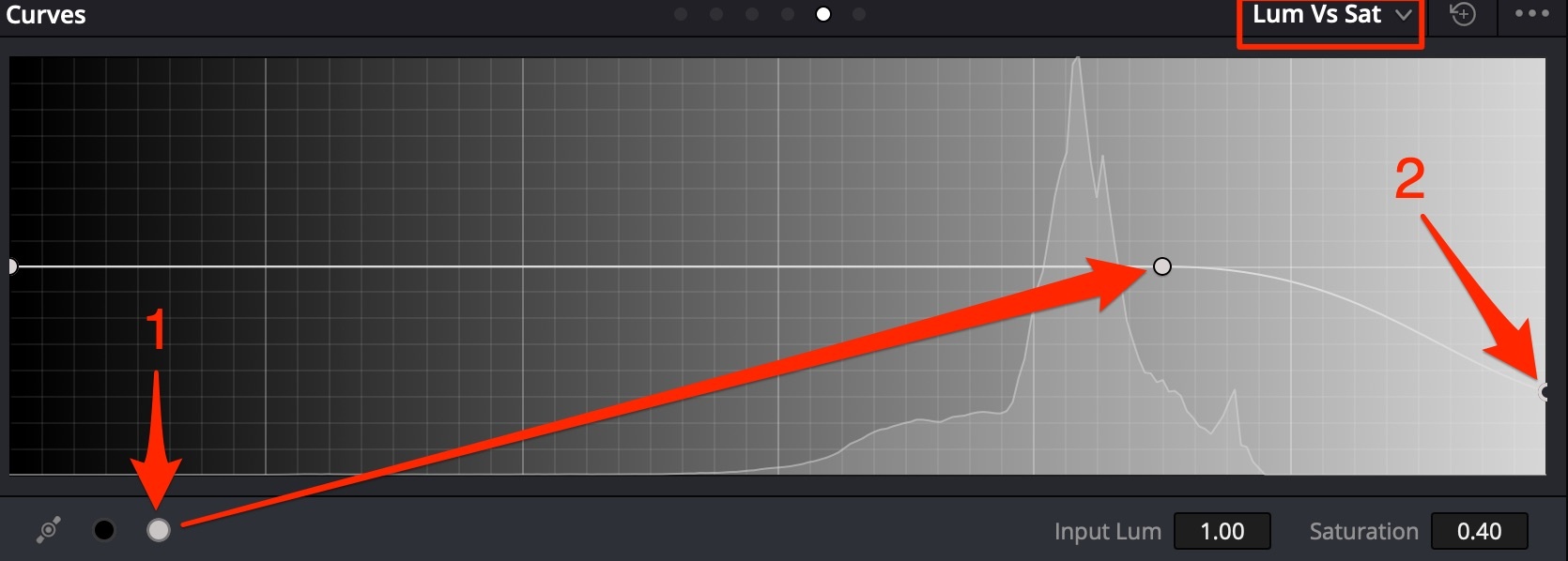

- Isolate highlights by luminosity;
- Bring saturation level in highlights down to remove color.
Node Structures
Color Correction Structure
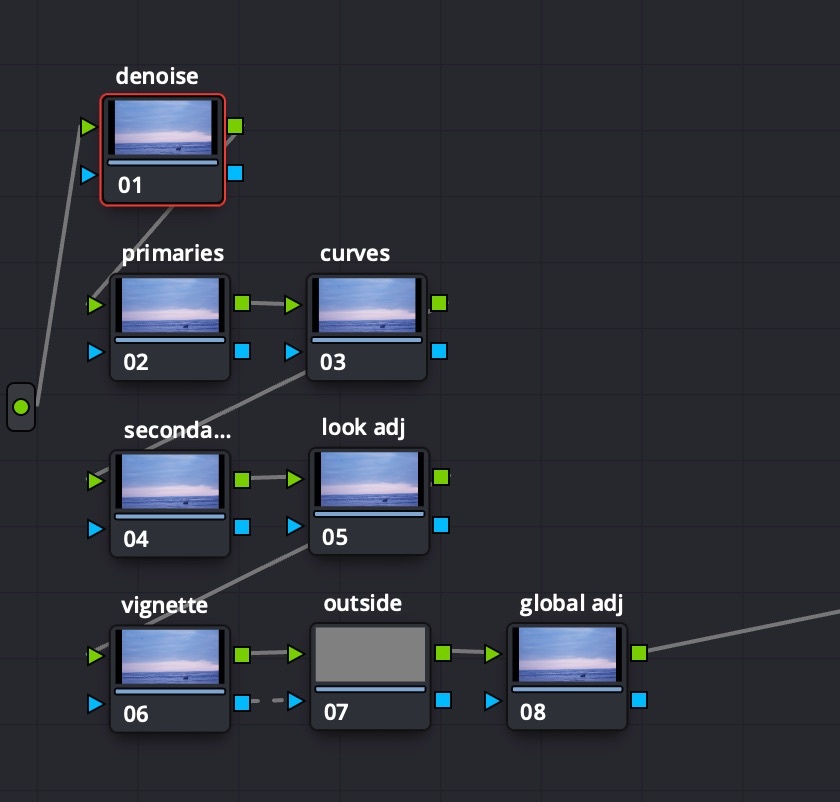

Color Correction structure contents:
- global denoise to reach pristine look for selection
- node for primaries
- node for curves
- basic secondaries + additional secondaries nodes
- vignette node, then Add Node → Outside Node, then finally the global look
Color Grading Structure
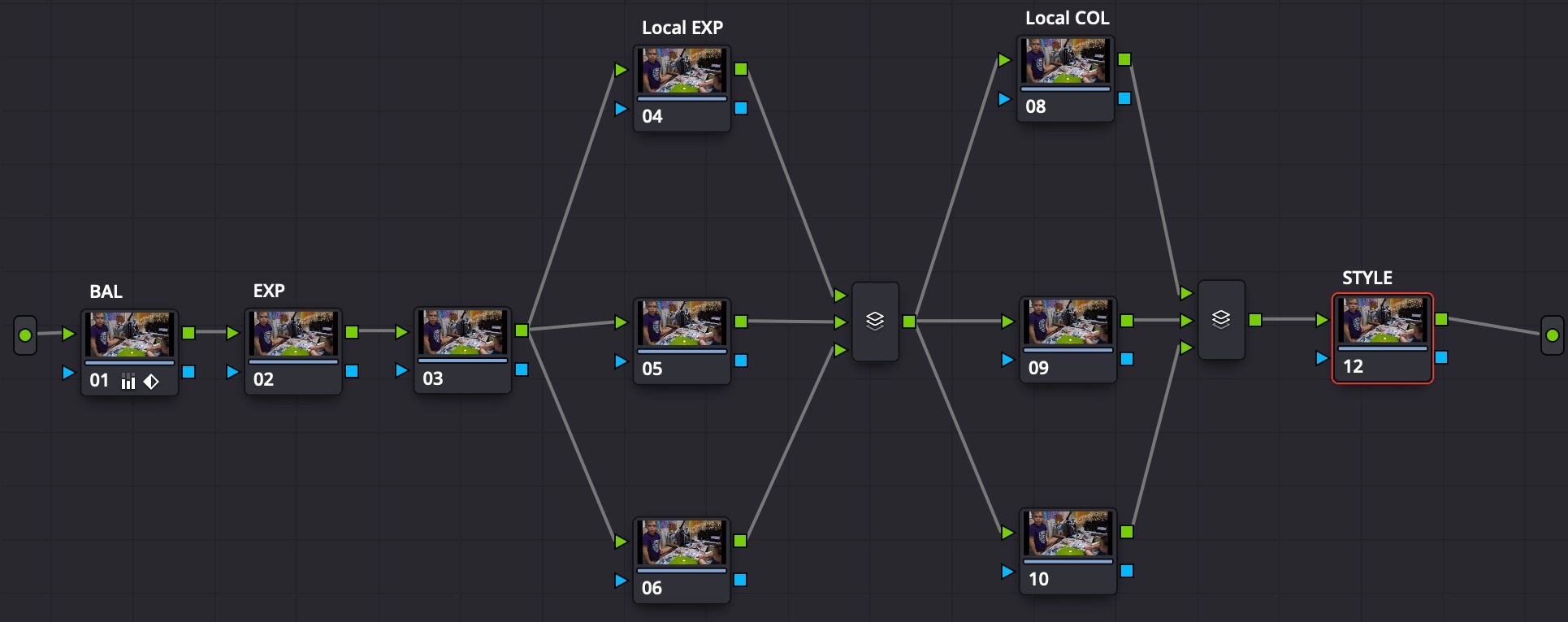
 Color Grading structure contents:
Color Grading structure contents:
- 3 global corrector nodes: color balance, global exposition, misc global node (noise reduction?)
- 3+ local exposition corrector nodes: use masks for areas and add light, like lighting up the face
- Parallel mixer with 3 inputs
- 3+ local color corrector nodes: use masks for areas and change saturation, like de-saturating items with bright colors, which may drag unwanted attention
- Parallel mixer with 3 inputs
- 1 corrector node with a combination of LUTs to produce a special look (color grading for drama / atmosphere / mood goes here)
Parallel Nodes
Changes in parallel nodes are made to the image with the same intersection, as if the nodes were in sequence (Serial type). The difference is that all parallel nodes read data from one initial node, while in serial sequence the next node reads data from previous node with all corrections applied on the previous step.
Node Layers
Layers are parallel nodes, but work in opposite direction: lowest layer has the highest precedence. Layers can be composited using connecting node settings.
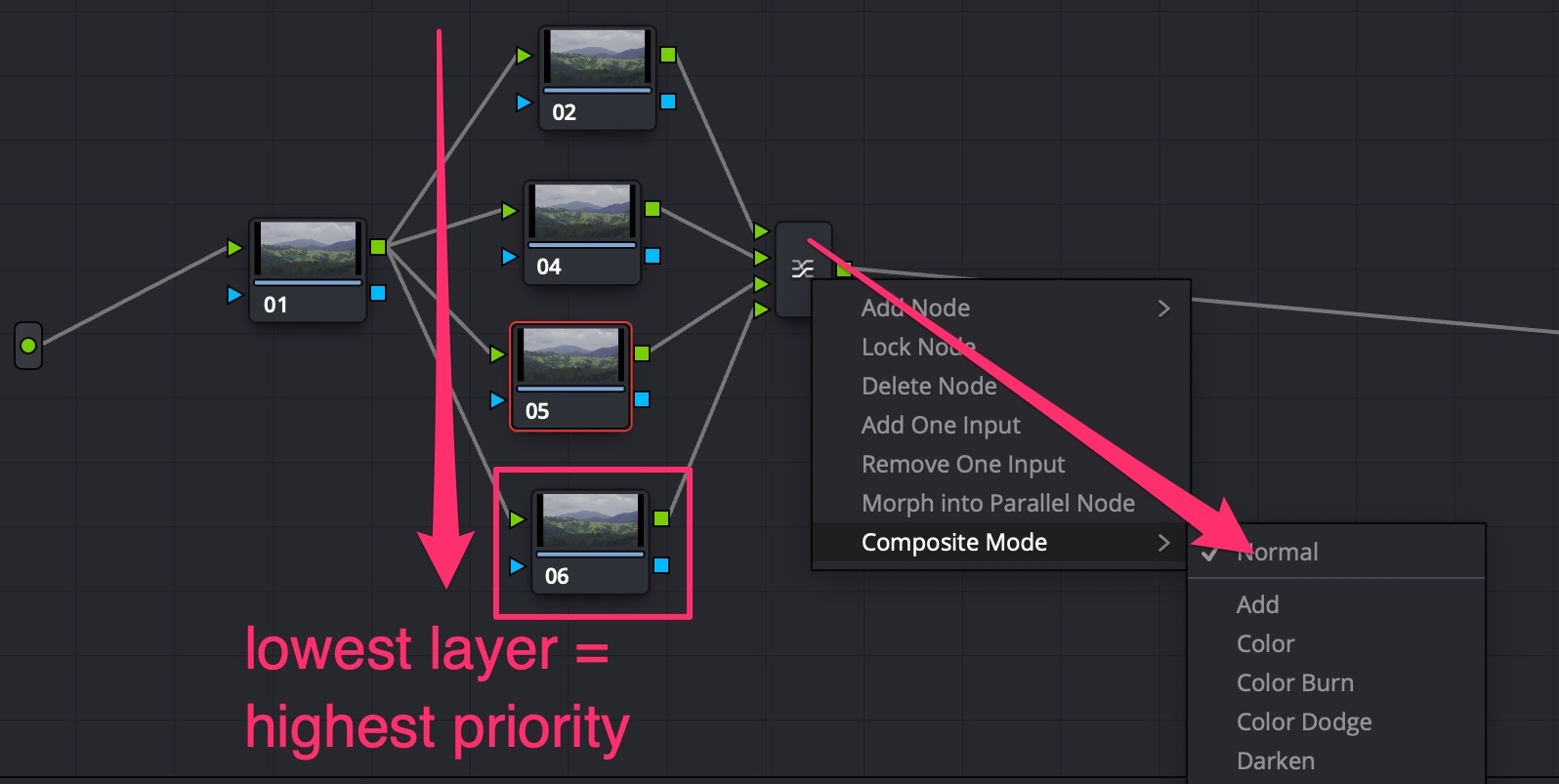

Node Sequence
Nodes sequence matters
- Create 2 nodes: in the first darken image using a LIFT wheel. In the second node make it red with the LIFT wheel and raise Saturation to 100%;
- Make a second version with nodes in reverse sequence;
- See the difference: if darken is first, then more areas become red using the second node than vice-versa.
Tip
Instruments sequence also matters: in the Color Wheels section, Lift/Gamma/Gain wheels are applied BEFORE the general Offset wheel.
Contrast sequence matters
When you use a node to make stronger contrast on a footage, you basically stretch the image info between Dark & Light boundaries. If you create a second node after the “contrast creation” one, you will be changing the resulting stretched image data, and the changes will be more subtle and soft.
Skin and Sky
Skin Exposure
For dark skin (african-american) use contrast+pivot to the left to lighten up, while maintaining contrast:
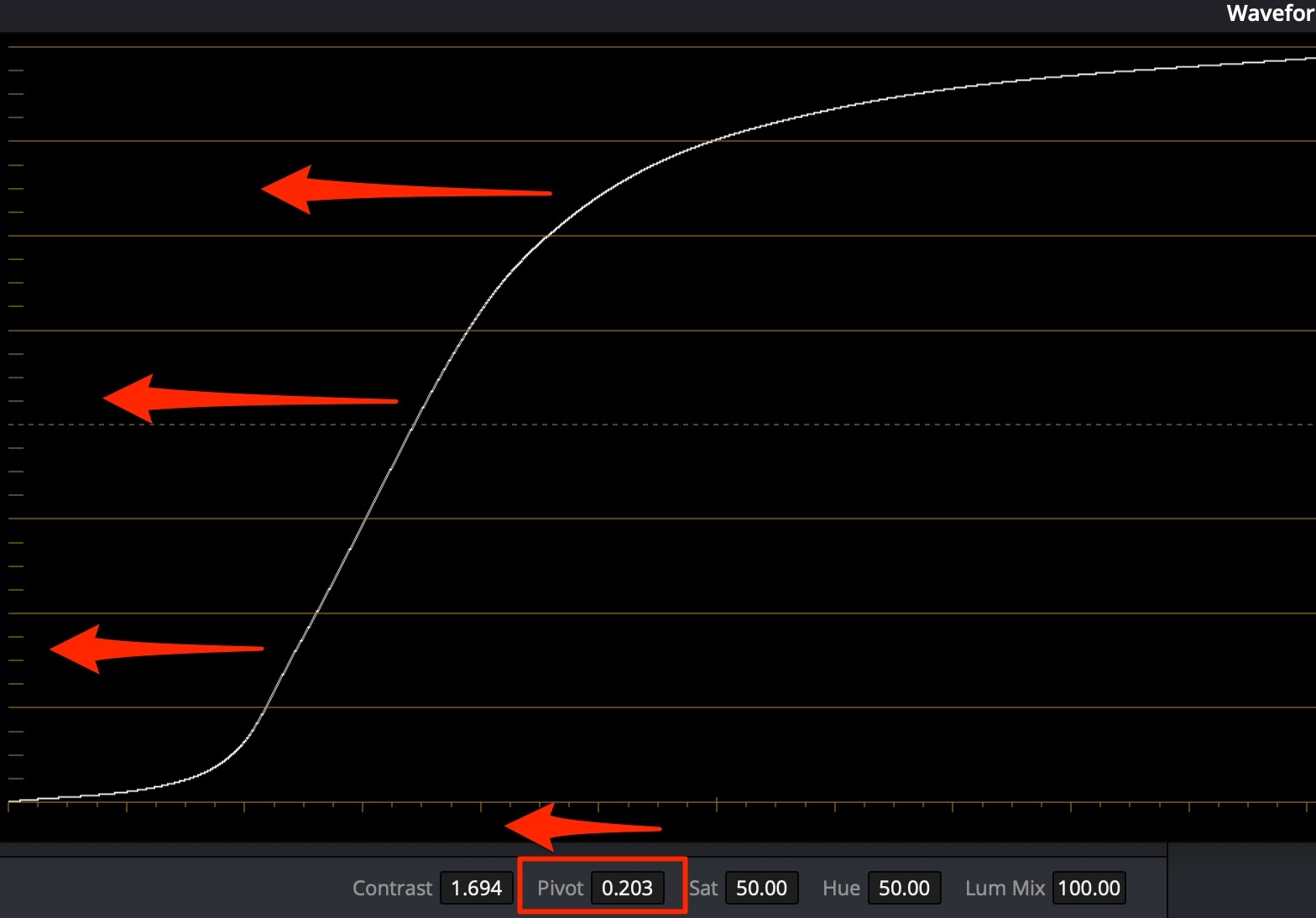

For pale skin (caucasian) use contrast+pivot to the right to darken, while maintaining contrast:
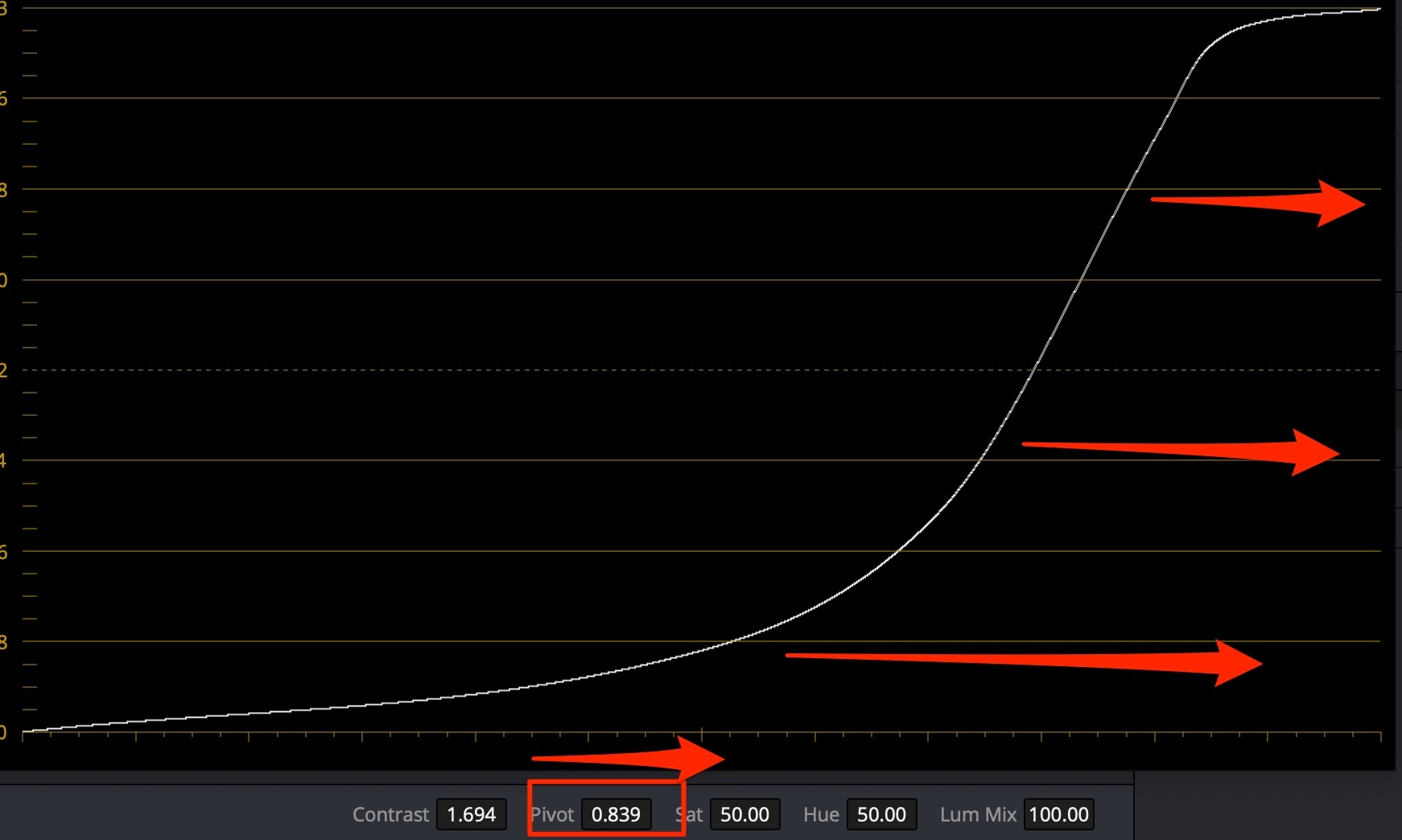

Tip
If you lift the lower midtones, you need to make up for Saturation loss - raise it.
Glow
Use Glow OpenFX plugin on skin selection to add a bit of skin light (Shine Threshold = ~0.6)
(Quick) Skin Retouch
Skin tones are “Midtones”. So use Qualifier and masks to select the skin, and subtract the eyes & brows & mouth.
- Raise Color Wheels → (page 2) Midtone Detail (MD) for boys to underline harshness and manliness;
- Lower Color Wheels → (page 2) Midtone Detail (MD) for girls to smooth out their faces (around -80);
- Lower overall effect of filter to make it look more natural Key → Key Output → Gain = 0.8 - 1.0
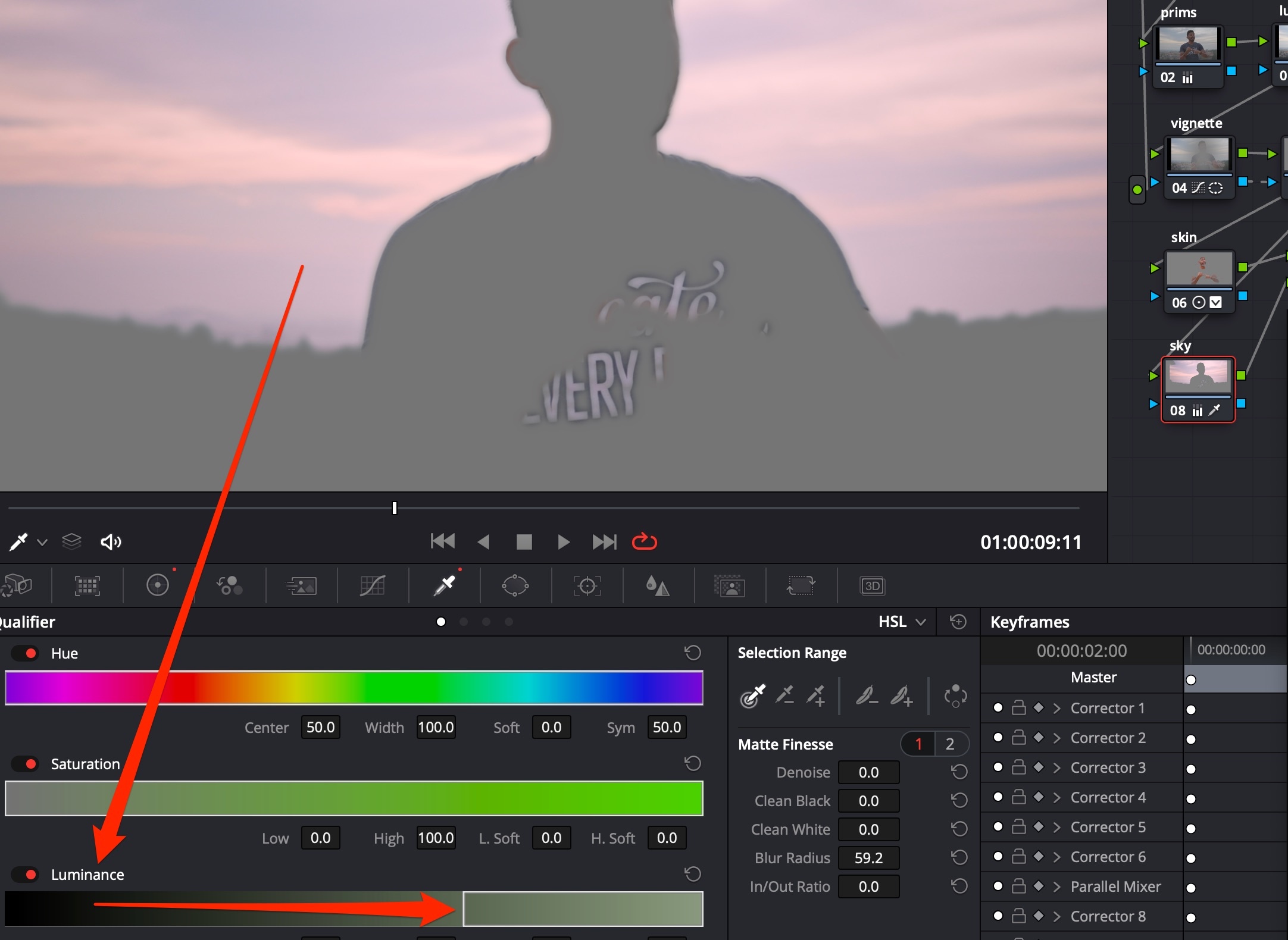
Sky Selection
Use Luminance qualifier for the cleanest sky selection.

Vignette
- Хорошо работают при неоднородном фоне. На однородном они слишком очевидны
- Делают видео более объёмным, отделяют передний и средний планы от заднего
Способ создания 1
- OpenFX → ResolveFX Stylize → Vignette
Способ создания 2
- Обычно виньетки применяются на уровне Timeline
- Добавить новую ноду (ALT+S), добавить к ней круговую маску
- Добавить outside node (ALT+O), с помощью колец Color Wheels опустить Gain и Saturation, в разделе Key снизить Key Output → Gain до 0.8-0.9, чтобы смешать с оригинальной картинкой
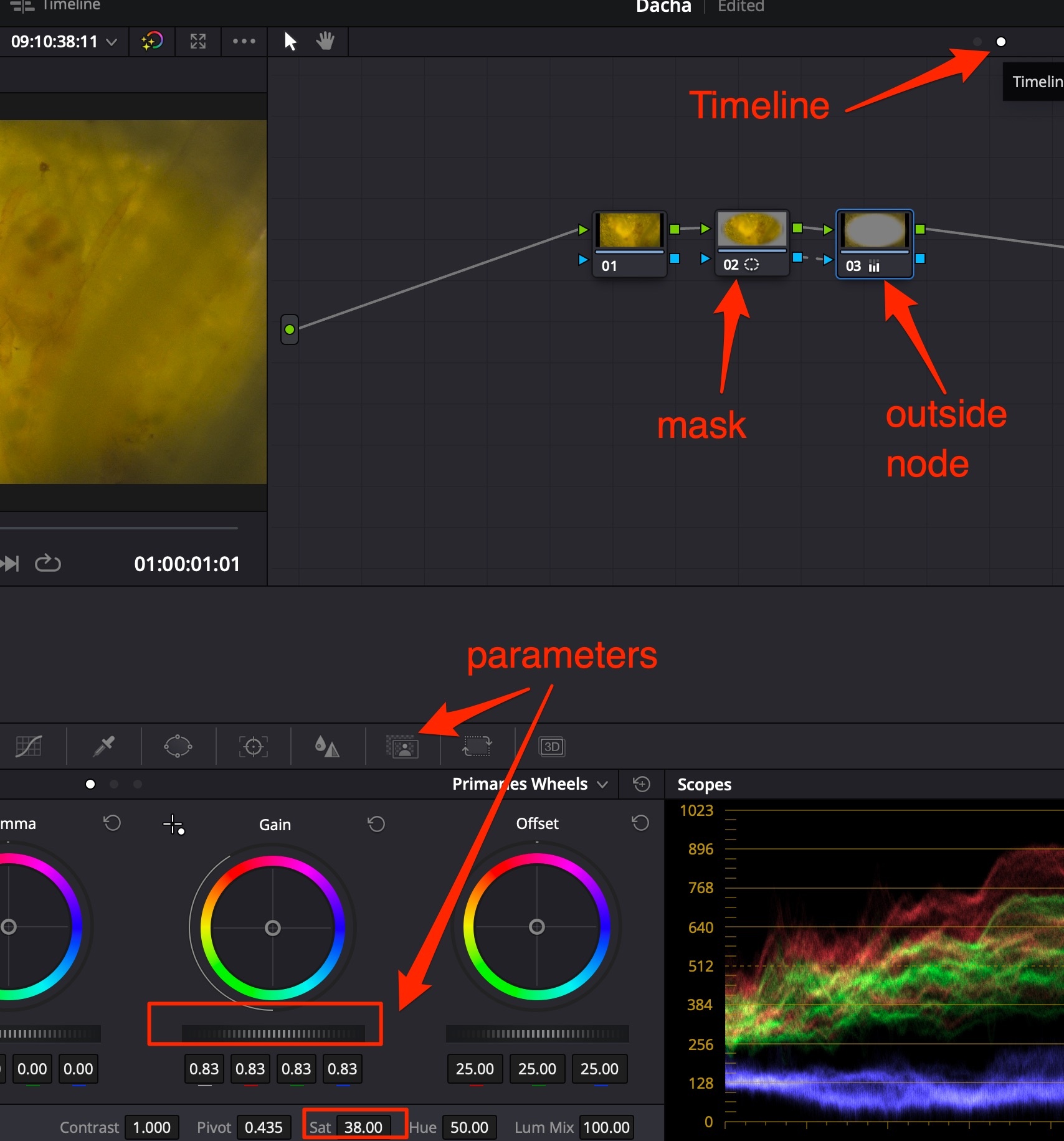
 Способ 2 лучше чем 1, т.к при способе 1 по углам создаются чёрные области с растушёвкой, в то время как при способе 2 происходит “multiply” видеопотока на себя с коррекцией = такой способ даёт менее “грязный” результат.
Способ 2 лучше чем 1, т.к при способе 1 по углам создаются чёрные области с растушёвкой, в то время как при способе 2 происходит “multiply” видеопотока на себя с коррекцией = такой способ даёт менее “грязный” результат.
Способ создания 3
- Создать ноду Vignette;
- Создать круговую маску на субъекте, с высокой мягкостью (Soft = 25);
- Зайти в Curves, основную кривую опустить примерно по центру вниз;
- Добавить outside node (ALT+O),
- В этой ноде зайти в Curves, основную кривую немного поднять (либо создать обратную S-кривую, поднять лишь тени), чтобы высветлить субъекта.
VR360
External links:
Подготовка видео
Для Insta360 X2 - видео 6K@30FPS:
- Собрать видео и экспорировать из родной программы в 360VR-ProRes 422 формат.
Поставить галочки FlowState, Lock Direction (для видео с рук или с дрона, для видео со штатива не надо).
- Очистить видео от артефактов и увеличить до 8K. С помощью Topaz Video AI сделать 2 прохода:
- Первый проход с алгоритмом Artemis DeHalo, размер 100%, добавить Grain (Size=1);
- Второй проход с алгоритмом Gaia High Quality, размер 133,33%.
Подготовка проекта
Разрешение:
- 3840x1920 - для соц сетей, интерактивного просмотра с моб телефонов подойдёт
- 5760х2880 - для YouTube 6K показа
- 7680x3840 - для Youtube 8K показа
Проксирование (Optimized Media and Render Cache):
- Proxy media resolution = Quarter
- Кодек = на Apple это Prores 422
- Указать папку для складывания видео Proxy.
Просмотр VR360
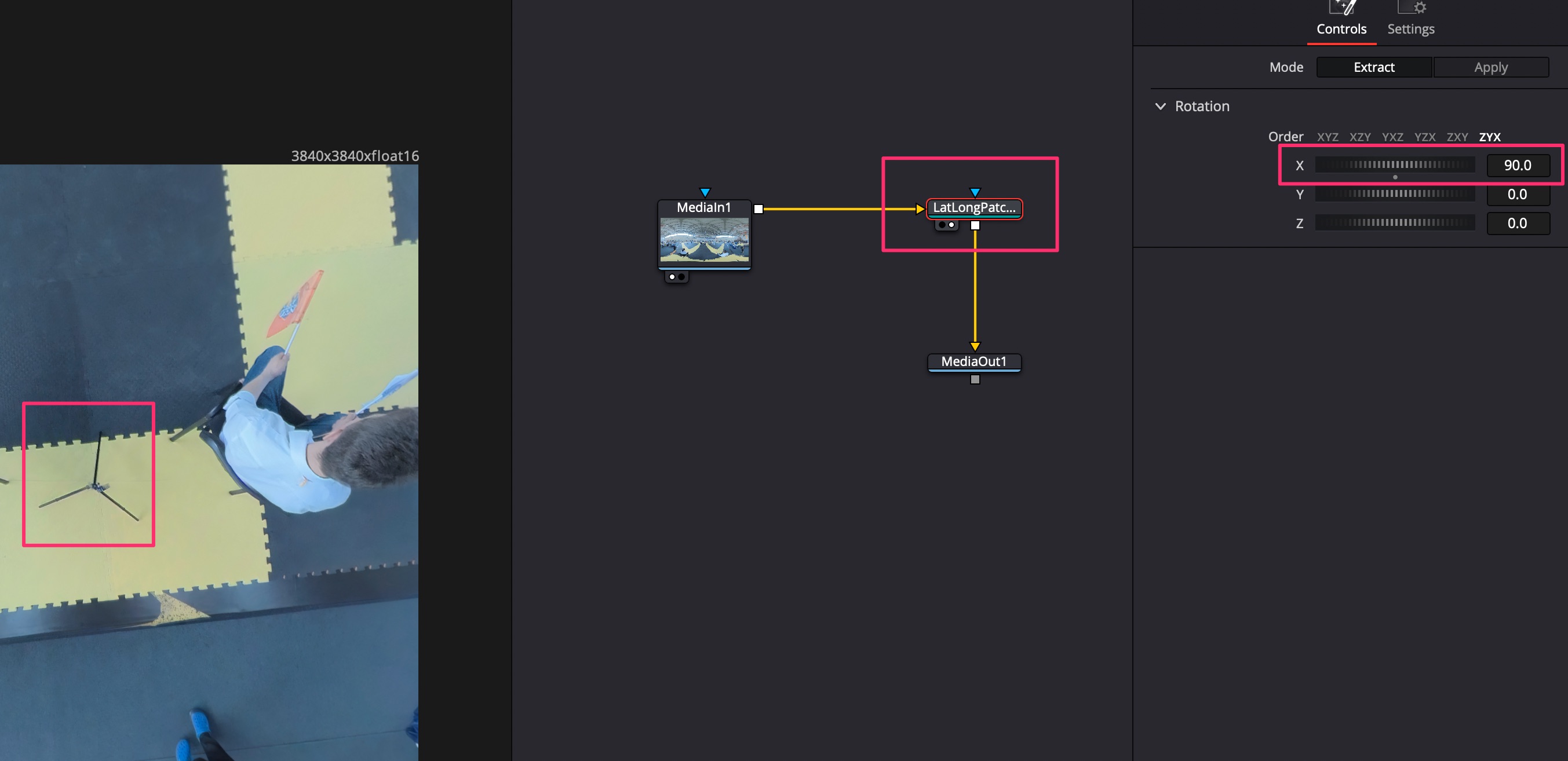
Положить видео VR360 на timeline. Далее перейти в комнату Fusion, нажать правой кнопкой на видео в окне и выбрать 360 View -> LatLog. После этого можно панорамировать с помощью ALT+средняя кнопка мышки.
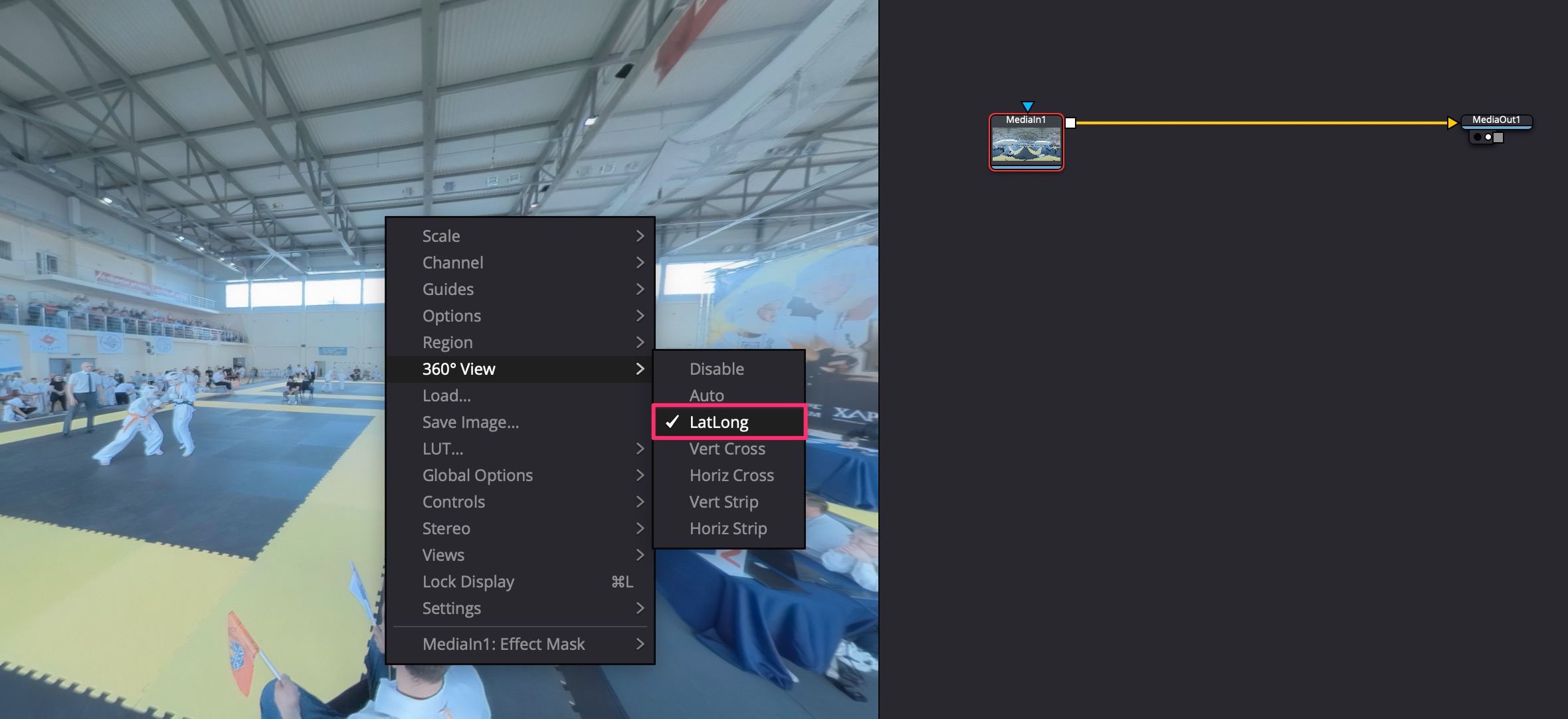
 Когда закончил панормирование, можно нажать правой кнопкой на видео в окне и выбрать Settings -> Reset Defaults
Когда закончил панормирование, можно нажать правой кнопкой на видео в окне и выбрать Settings -> Reset Defaults
Для ускорения просмотра выбрать режим отображения Proxy и отключить высокое качество.
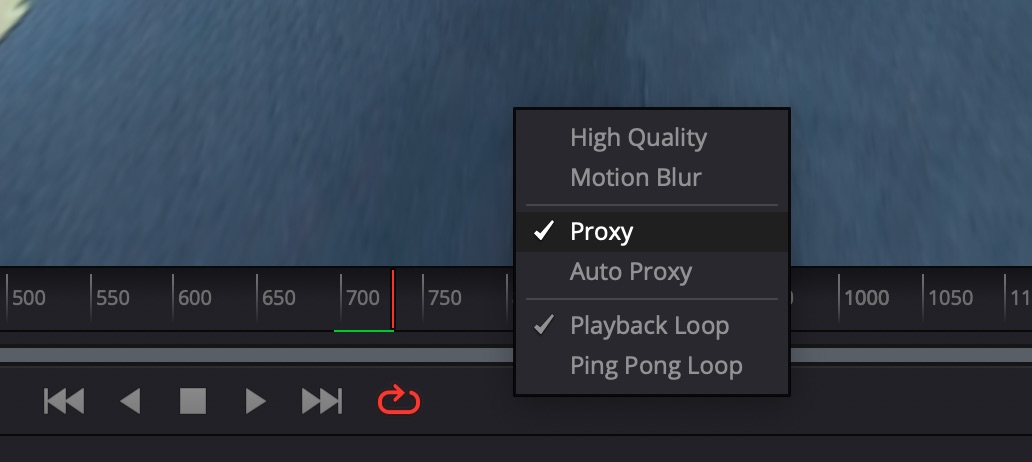
 Также в главном меню выбрать Playback -> Timeline Proxy Resolution -> Half.
Также в главном меню выбрать Playback -> Timeline Proxy Resolution -> Half.
Смена направления на север и завал горизонта
Для начальной ориентации камеры нужно добавить ноду PanoMap. Далее перевести отображение обоих окон с видео на эту ноду. Выбрать просмотр в одном из окон 360 View -> LatLog. С помощью настроек PanoMap поменять ориентацию по осям.
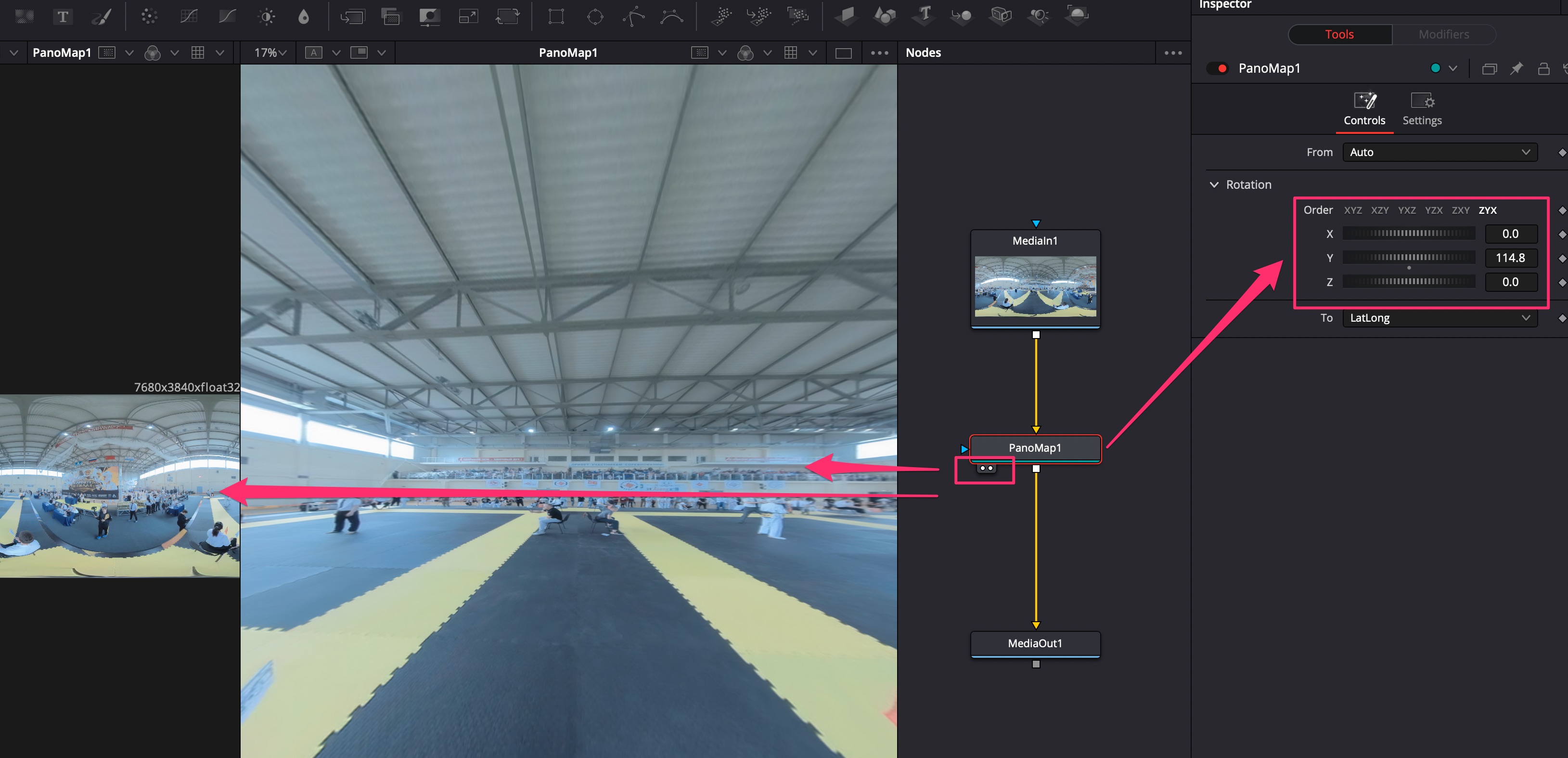
 При съёмке с дрона может быть завал горизонта: исправить можно путём анимации осей. XYZ в настройках PanoMap.
При съёмке с дрона может быть завал горизонта: исправить можно путём анимации осей. XYZ в настройках PanoMap.
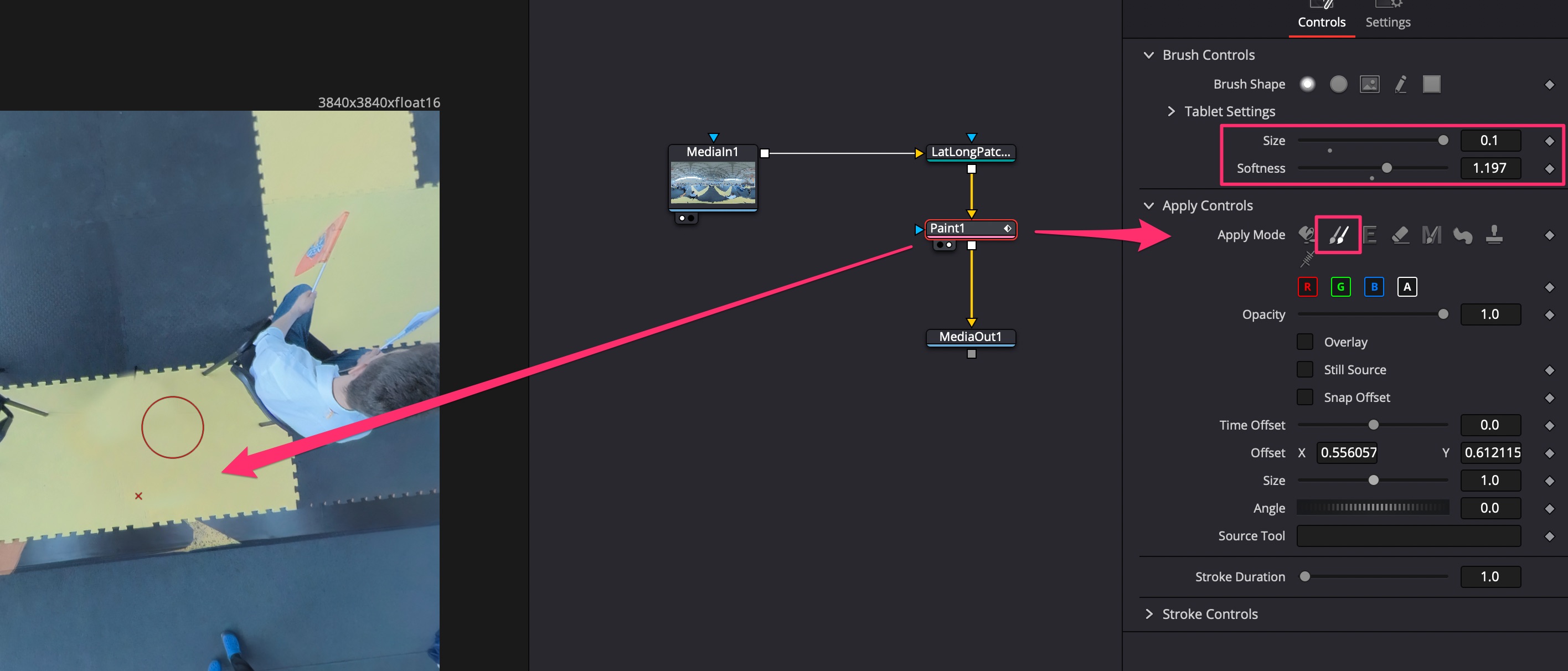
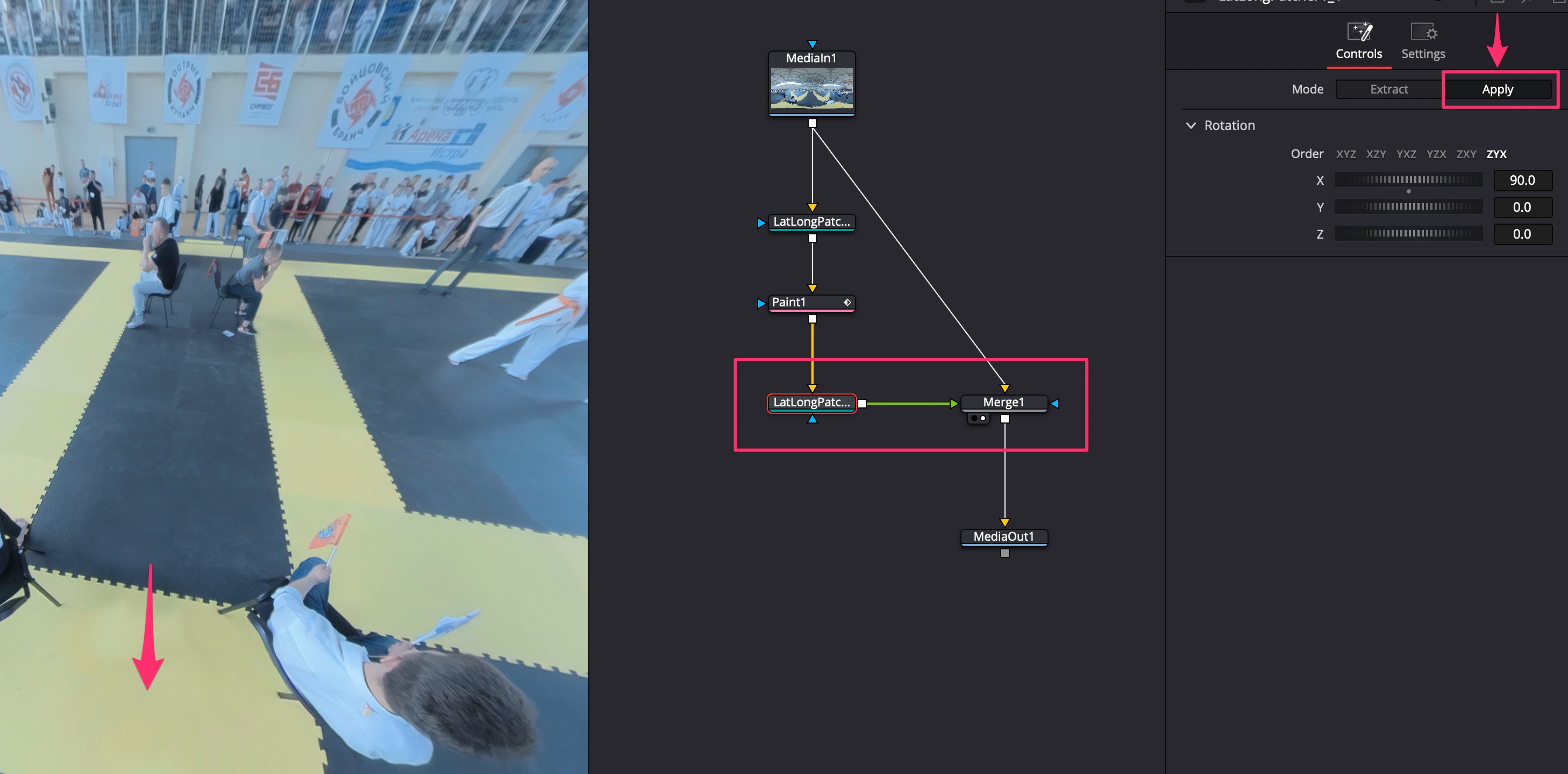
Редактировать - убрать штатив/дрона
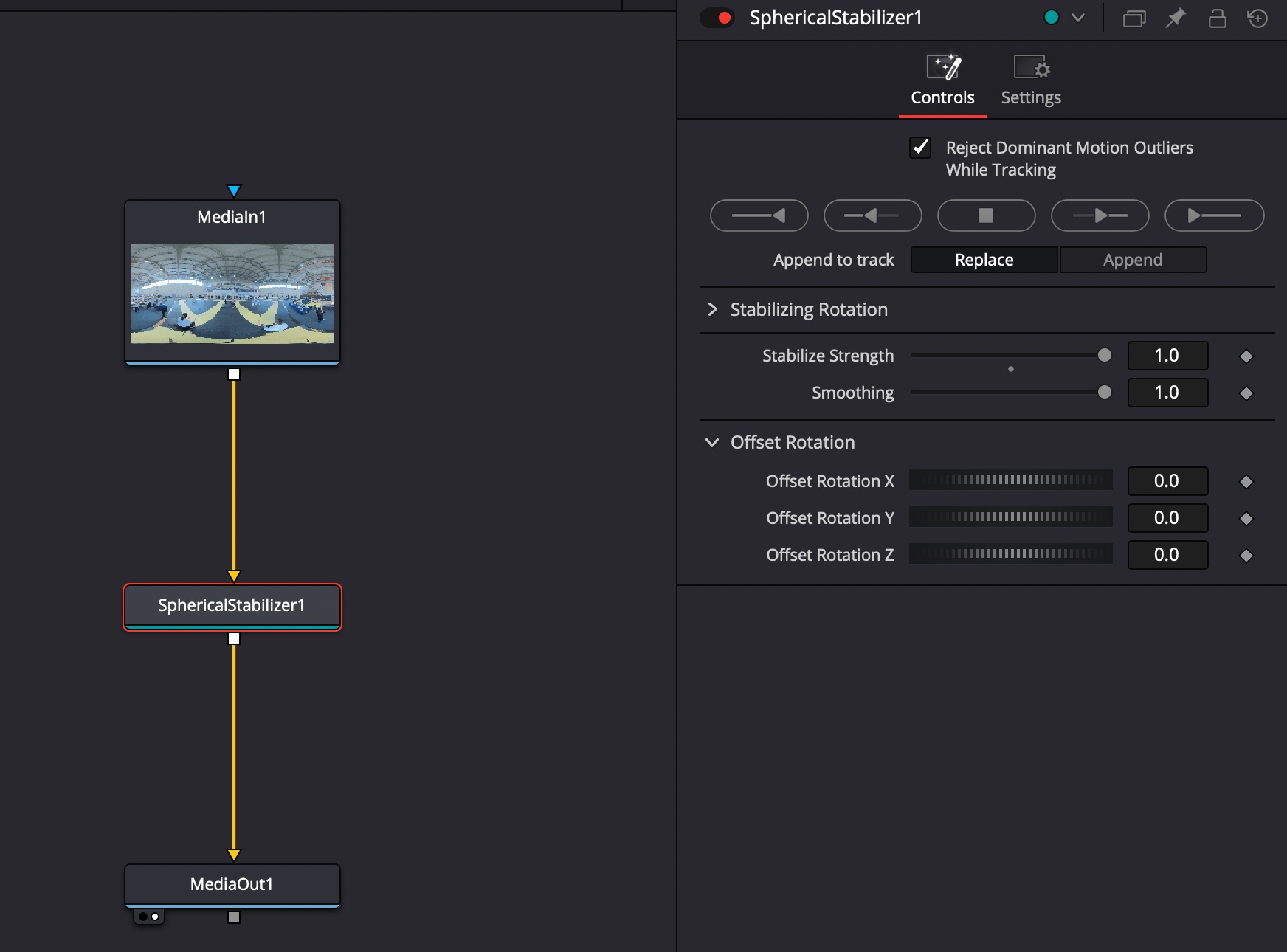
Стабилизация VR360
В команте Fusion добавить ноду Spherical Stabilizer. Stabilize Strength = 1, Smooting = 1. Произвести трекинг всего видео.

Создание объектов в 3D видео
- Добавить ноды Spherical Camera, Merge 3D, Renderer 3D, Shape 3D;
- У ноды Shape 3D установить Shape = Sphere и соединить в неё Media In.
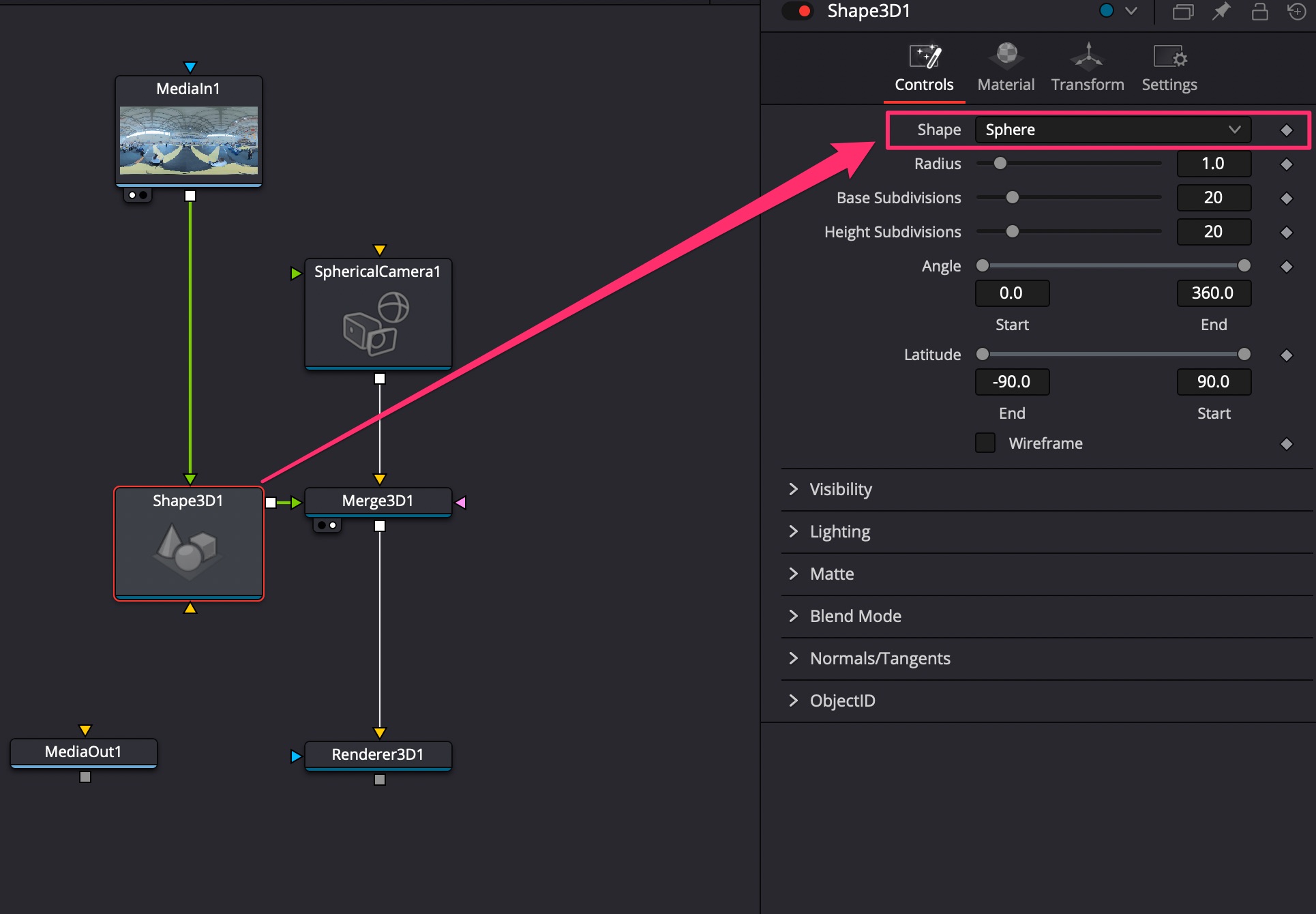

- Подключить вывод видео в окно просмотра в ноде Merge 3D;
- Можно панорамировать в окне просмотра с помощью ALT+средняя кнопка мышки;
- У ноды Shape 3D установить Radius = 10, чтобы “войти в сферу”, увеличить Base Subdivisions = 60 и выше, чтобы убрать полигональные артефакты;
- Выделить ноду Render 3D, включить отображение видео в 1 окно. Обратить внимание, что точка обзора поменялась. Нажать CTRL+G, чтобы отобразить перекрестье и направляющие;
- У ноды Spherical Camera во вкладке Transform по оси Y подвинуть ось камеры, чтобы установить её в нужном направлении;
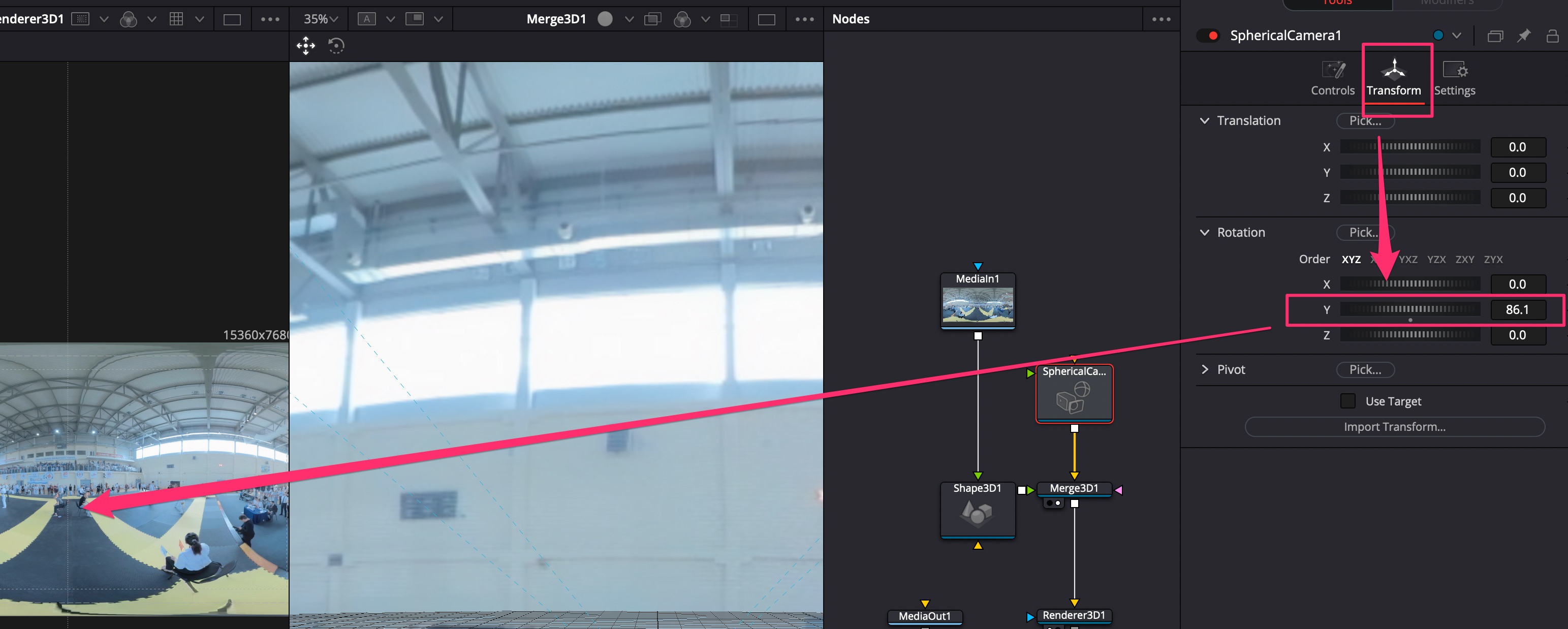

- Проверить, что включено низкое качество показа, Proxy, в главном меню выбрать Playback -> Timeline Proxy Resolution -> Quarter для ускорения Renderer 3D;
- Добавить ноду Text 3D, написать текст, подключить к ноде Merge 3D;
- Использовать направляющие перемещения и поворота для правильной ориентации текста по отношению к камере;
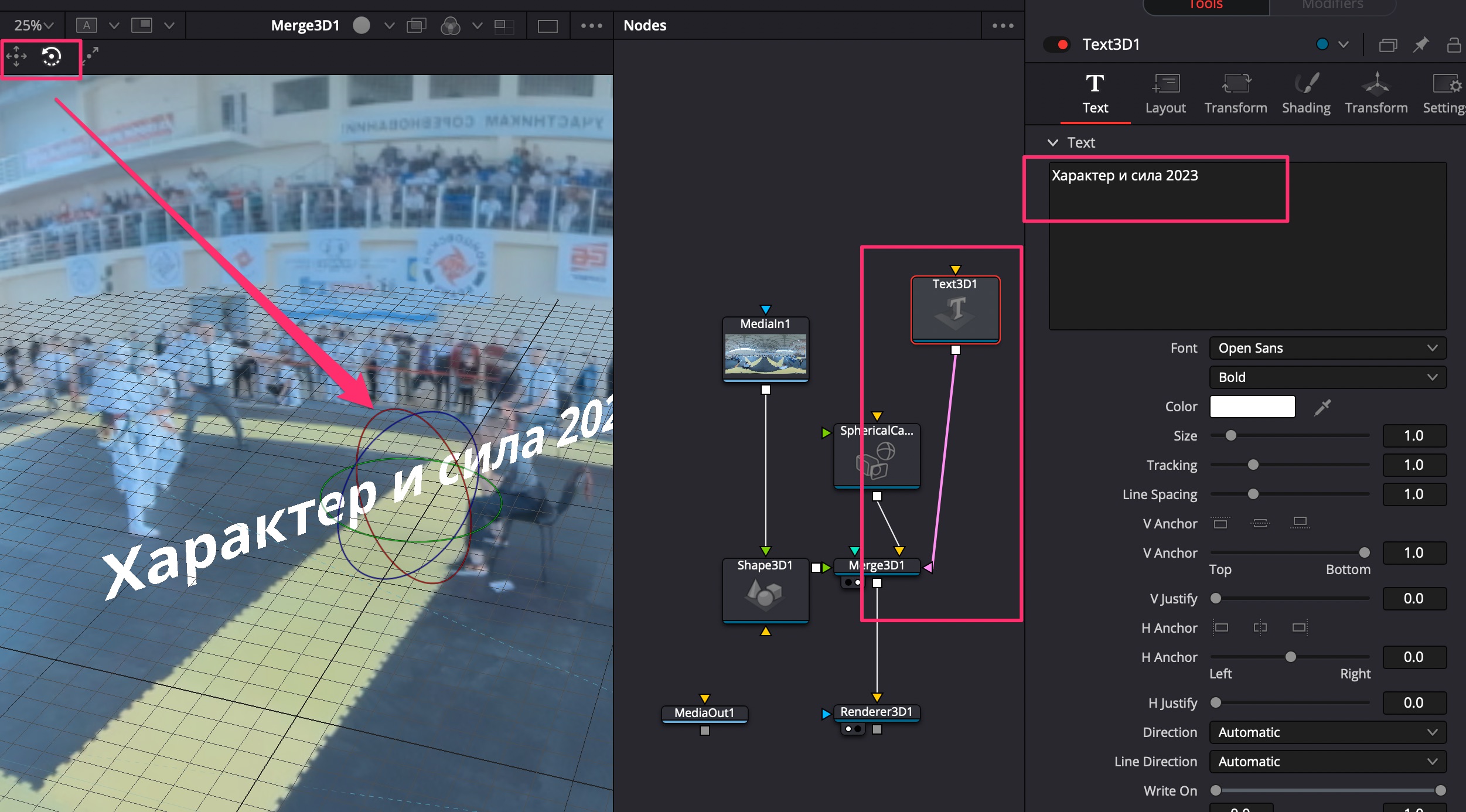

- Перейти в настройках Text 3D во вкладку Transform, добавить ключи анимации по осям XYZ;
- Включить в интерфейсе Fusion вкладку Spline, включить в ней все оси анимации, нажать CTRL+F для масштабирования графиков анимации в экране;
- Сделать анимацию по времени, нажать на ключевые кадры и усиками Безье придать плавность анимации;
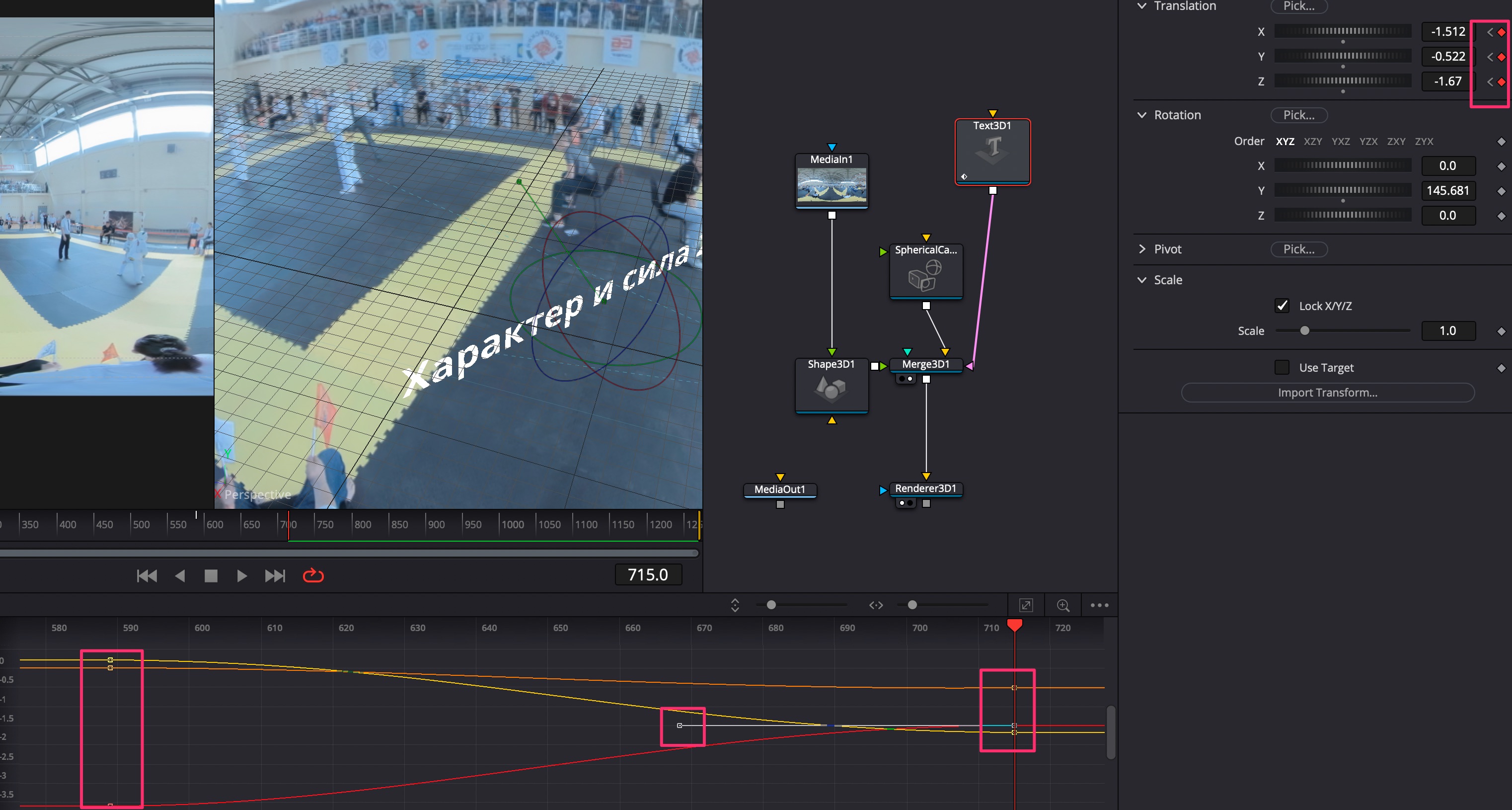

- Соединить выход Renderer 3D с Media Out;
Отображение 2D текста и графики в 3D
- Добавить ноды Text, Background, соединить их через ноду Merge, после чего внести в 3D через ноду Image Plane 3D;
- В настройках Image Plane 3D -> Transform регулировать масштаб Scale = 3;
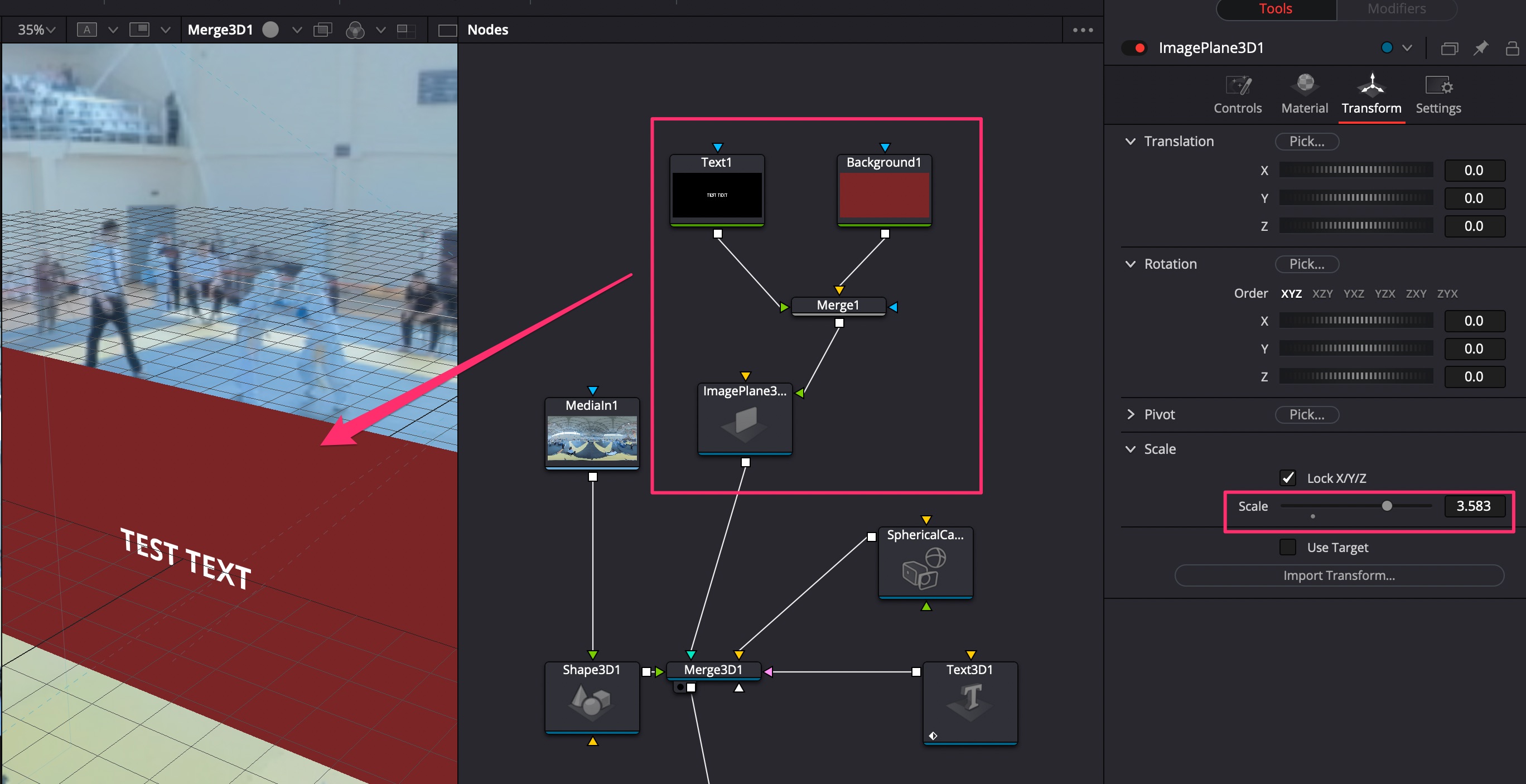

- Можно таким же образом перестаскивать из Media Pool обычные видеоролики и подключать через Image Plane 3D.
Экспорт видео
Для 6К - 8К видео выбирать кодек H.265.
Битрейт Quality = 100000 Kb/s для большей плавности картинки.
Warning
Для шлема Oculus Quest 1 нужно указывать не более чем Quality = 60000 Kb/s.
Включить Advance Settings -> Force Sizing to highest quality, Force debayer to highest quality.
DaVinci Resolve не делает инъекции метаданных в видео, поэтому для публикации на Youtube нужно это сделать отдельно (для Facebook этого делать не нужно - можно просто закачать видео, и оно будет VR360).